How to use Virtual Machine High Availability (VMHA) in Virtualization Station?
Applicable Products
- QuTS hero h5.3.0 or later
- Virtualization Station 4.0 Beta or later
Introduction
VM High Availability (VMHA) is a feature in Virtualization Station that enables automatic failover of virtual machines between two QNAP NAS devices. It helps ensure service continuity in case of hardware failure by minimizing downtime.
This tutorial guides you through the complete setup process, including preparing your environment, creating a VMHA device pair, creating and managing VMHA groups, configuring failover, and troubleshooting common issues.
VMHA Requirements
System Requirements
| Component | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Operating system | QuTS hero h5.3.0 or later on both NAS devices. Note For best compatibility, it is recommended to use NAS devices that are running the same version of QuTS hero. |
| Processor | Both NAS devices must use CPUs from the same vendor (e.g., Intel® or AMD®). |
| Memory | The destination NAS must have enough memory to run the migrated virtual machines from the source NAS during failover. |
| Storage | Both NAS devices must have sufficient space for Virtualization Station to create a shared folder to store the VMHA disk images. Disk images must be stored on the NAS’s internal storage only, and external storage cannot be used. |
Network Requirements
| Component | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Network connections | At least two independent network connections are required between the two NAS devices. These must be on different subnets: one for the management link and one for the availability link (used for data synchronization). |
| IP addresses | All interfaces used for HA must use static IPv4 addresses. IPv6 and VLAN settings must be disabled. |
| Firewall ports | If a firewall is in use, ensure that TCP ports 16500-16550 are open between the two NAS devices to allow HA communication. For a complete list of service ports used by QNAP systems, see What network ports are used by QTS, QuTS hero, and QuTScloud systems. |
| Availability link | A network speed of at least 2.5 Gbps is strongly recommended, as link speed directly affects VM performance. For best performance, use a direct Ethernet connection between the NAS devices, avoiding switches when possible. |
| SSH service | The SSH service must be enabled on both NAS devices. For details, see Configuring SSH connections in the QuTS hero User Guide. |
Preconfiguration Requirements
- Configure compatible virtual switches on both NAS devices using Network & Virtual Switch. While the virtual switch names do not need to match, the interface assignments and network settings must be aligned. For details, see Virtual switch configuration in the QuTS hero User Guide.
- Ensure that both NAS devices are running the same version of QuTS hero. If the firmware versions differ, VMHA might not function as expected. To update the NAS firmware, see Firmware update in the QuTS hero User Guide.
- Configure both NAS devices to use the same NTP server for time synchronization. For details, see Configuring time settings in the QuTS hero User Guide.
- Ensure required ports are open or forwarded if using firewalls or NAT.Warning
- VMHA cannot be enabled if either NAS is part of a Hero HA cluster. Ensure that both devices are in standalone mode by unpairing any existing Hero HA configuration before proceeding.
- Both NAS devices must run the same version of Virtualization Station. If the versions differ, such as after a system or app update, all HA protection groups will be paused automatically until version consistency is restored.
Procedure
Setting up virtual machine high availability (VMHA) involves three main steps to ensure that your virtual machines remain operational if the source NAS becomes unavailable.
- Create an HA Device Pair: Connect two NAS devices to form a high availability group. This step only pairs the two NAS devices, including verifying requirements, configuring the network connection for synchronization, and binding the virtual switches used by the VM. It does not include the future HA synchronization direction for the VMs.
- Create an HA Availability Group: Defines which virtual machine to protect, sets up the synchronization direction, and allocates storage on both NAS devices. This group manages the backup and recovery process for the VM.
- Configure the Failover Policy: Specifies the conditions that will automatically trigger failover, such as hardware issues or high resource usage.
Completing these steps ensures that selected virtual machines can be automatically restarted on the destination NAS in the event of a failure, minimizing service disruption.
Create an HA Device Pair
- Open Virtualization on the local NAS.
- Go to High Availability.
- Click Configure Paired Devices.
The Configure Paired Devices for VM Availability wizard opens. - Click Start.
- Review the requirements for paired devices.
- Click Next.
- Configure the local device settings.ImportantIf you are using a direct physical connection (such as a dedicated Ethernet cable between the two NAS devices), do not select the adapters to configure the M-link (management link). Assigning an IP address in this scenario can cause Virtualization Station to report connection errors.
- Specify the IP address of the local device.
- Specify the device port number.
- Optional: Select Use SSL connection.
- Specify the device username.
- Specify the device password.
- Click Next.
- Configure the remote device settings.
- Specify the IP address of the remote device.
- Specify the device port number.
- Optional: Select Use SSL connection.
- Specify the device username.
- Specify the device password.
- Optional: Click Test.
Virtualization Station tests the local and remote device connection.
- Click Next.
The Configure Paired Devices and Their Credentials window appears.
- Review the local and remote device settings.
- Click Next.
The Configure Availability Link (A-Link) window appears.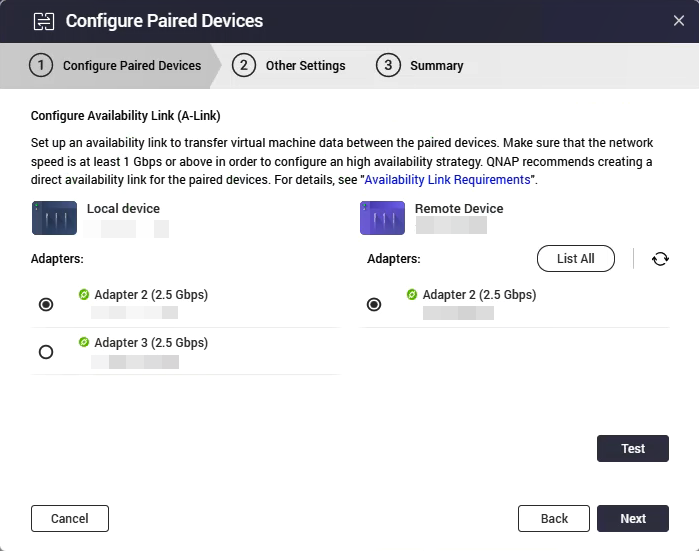
- Select the A-link adapters for the local and remote device.NoteClick List All to view all the adapters linked to the local or remote device.
- Click Test.
Virtualization Station tests the A-link connectivity. - Click Next.
The Configure VM Network Settings window appears. - Configure the VM network settings for the paired devices.
- Click Add.
The Pairing VM Networks window appears.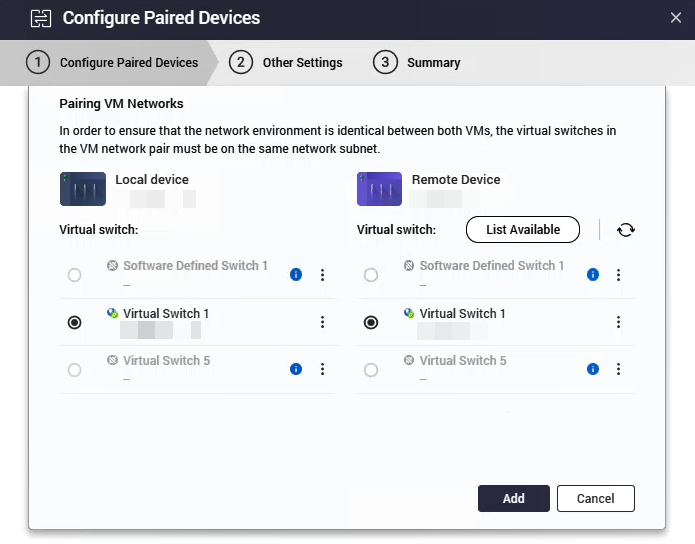
- Select the virtual switches for the local and remote devices.Important
- The virtual switch or switches you select in this step determine which VMs can be protected by HA. Only VMs connected to the selected virtual switches will be available for selection.
- The wizard filters out incompatible virtual switches automatically. This includes switches that are not linked to a physical network adapter, reserved for system use (such as Docker or LXD), or configured with NAT or DHCP server functions.
If a virtual switch is missing from the list, review its settings in Network & Virtual Switch.
- Click Add.
Virtualization Station adds the virtual switches to the paired devices.
- Click Add.
- Click Next.
The Other Settings window appears. - Configure the failover policy settings.
For details, see Configuring Failover Policy Settings. - Click Next.
- Review the settings.
- Click Finish.
Virtualization Station creates the HA device pair.
To manage the configured VMHA device pair, go to High Availability > Paired Devices.
- Go to Actions > Edit Paired Devices to update the configuration.
- Go to Actions > Unpair Paired Devices to remove the pairing.
Configure an HA Availability Group or Plan
- Log in to your local NAS.
- Open Virtualization Station.
- Next to Create Virtual Machine, click
 .
. - Click Create Availability Group.
The Availability Groups window appears. - Click Start.
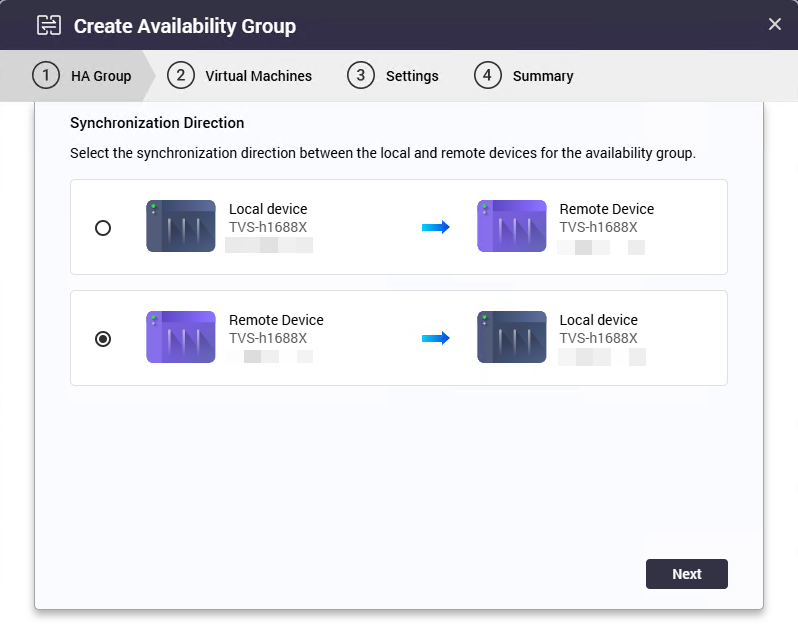
The Create Availability Group window appears. - Select the synchronization direction.
 Note
NoteThe synchronization direction defines which NAS acts as the source and which NAS receives the VM data as a high-availability backup. The list of virtual machines displayed during the selection step depends on the chosen source NAS.
- Click Next.
- Configure the HA group settings.
- Specify an HA group name.NoteA shared folder with the same name as the HA protection group is created in the selected storage pool on both the local and remote NAS devices. Ensure that the folder name is unique on each device to prevent naming conflicts.WarningDo not rename this folder for any VM that is already protected, as this may cause unexpected issues.
- Select the source device storage pool.
- Select the destination device storage pool.
- Specify the allocated quota for shared folder.NoteClick Use Available Pool Capacity to automatically assign the smaller of the available capacities from the selected local and remote storage pools.
- Click Create.
The High Availability (HA) Group Configuration window appears. - Verify the configured group settings.
- Specify an HA group name.
- Click Next.
The Virtual Machines window appears.
- Under the source device (local or remote device), click List Available.
- Select one or more virtual machines to include in the VMHA deployment.
- Click Next.
The Settings window opens. - Optional: Select Automatically resume the plan.
This option automatically restarts the HA plan after a reboot or interruption. - Click Next.
The Summary window opens. - Review the HA group settings.
- Click Create.
Virtualization Station creates the HA availability group.
Configure Failover Policy Settings
- Open Virtualization Station.
- Go to High Availability > Failover Policy.
- Configure the monitoring interval. This defines how frequently the system checks for failover conditions.
- Optional: Under Triggered Events, select the conditions that should trigger a failover. You can configure the following settings:
- Backup power mode: Initiates failover when the device runs on an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS).
- PSU redundancy loss: Initiates failover when the redundant power supply unit is disconnected or malfunctioning.
- System fan failure: Initiates failover when a system fan is not functioning properly.
- CPU load average exceeds threshold: Initiates failover when average CPU usage exceeds a defined percentage over a set duration.
- Memory load average exceeds threshold: Initiates failover when average memory usage exceeds a defined percentage over a set duration.
- Disk health error: Initiates failover when a virtual machine disk experiences a health issue or when a shared folder volume encounters an error.
- Network virtual switch error: Initiates failover when the virtual switch encounters a network-related error.
- Click Apply.
Virtualization Station saves and applies the failover policy settings to all the VMHA availability groups.
VMHA Monitoring, Troubleshooting, and Diagnostics
Monitor and Manage VMHA Groups
You can view the status of all VMHA groups, perform actions such as pause, resume, edit, or delete, and monitor synchronization progress and resource usage across both NAS devices.
Perform VMHA Actions
After an HA protection group is created, you can monitor and manage its status from the High Availability > Plans page.
- Open Virtualization Station.
- Go to High Availability > Plans.
- Under Action, click
 .
. - Identify a VMHA group or plan.
- Perform any of the following VMHA plan tasks.
Task Description Switchover Switches VMs between two NAS devices while keeping them online and operational, without requiring a reboot or suspension. Pause Temporarily suspends VMHA synchronization and failover protection for the HA group. Delete Removes the VMHA group and disables protection for the associated VM. Resume Restarts VMHA synchronization and failover monitoring for the group. Edit Opens the VMHA group settings for configuration changes.
Status Descriptions
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
Normal | The VMHA group is operating normally with no issues. |
Syncing | Initial or scheduled synchronization is in progress between the source and destination NAS. |
Pause | Synchronization is temporarily halted. The availability group is not actively syncing, but its configuration is preserved. Note This state can occur automatically if Virtualization Station is stopped or the NAS is shut down. |
Warning | VMHA protection is still active, but one or more issues may affect failover. Review and address the underlying causes promptly. |
Error | One or more critical failures have occurred. The VMHA group is no longer functioning correctly and requires immediate attention. |
Diagnose and Troubleshoot Common VMHA Conditions
To ensure stable and reliable HA operation, monitor system conditions and avoid configuration changes that may affect failover readiness.
Common Warning Conditions
| Warning | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Insufficient memory on the destination NAS | The available memory on the destination NAS is not enough to start the protected VM during a failover. | Failover will fail unless memory resources are increased or freed. |
| Degraded availability link | The availability link throughput has dropped below 50 Mbps or latency has exceeded 1 millisecond. | Reduced sync performance and increased recovery point objective (RPO). |
| Device pair configuration issues | Misconfigurations such as unstable management links or subnet mismatches between paired Virtual Switches. | Failover reliability may be compromised if not corrected. |
Troubleshoot VMHA Group Issues
| Issue | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Virtualization Station version mismatch | Ensure both NAS devices are running the same version of Virtualization Station. Check App Center for updates. Restart the app if needed. |
| Insufficient CPU or memory on source or destination NAS | Check system resource usage on both the source and destination NAS. Failover may fail if either system lacks sufficient CPU or memory to complete the process. Shut down unused VMs or services to free up resources. If necessary, consider upgrading the system memory. |
| Slow synchronization speeds or high latency | Use a direct network cable between NAS devices, or assign the availability link to a dedicated, high-speed subnet. |
| Virtual switch pairing errors | Open Network & Virtual Switch and confirm both switches are on the same subnet and have no conflicting settings (e.g., NAT or DHCP). |
| Cluster fails to create or join | Ensure both NAS devices are not already members of another Hero HA or VMHA cluster. Unpair any existing clusters before proceeding. |
Manage VMHA Logs
You can view and download VMHA-related logs to assist with troubleshooting, auditing, or verifying the system’s failover behavior. These logs provide detailed records of synchronization events, status changes, and system alerts, helping administrators diagnose issues and maintain operational visibility.
- Open Virtualization Station.
- Go to High Availability > Logs.
- Perform any of the following tasks.
- Search logs: Enter keywords in the search bar to filter log entries by event type, VM name, or timestamp.
- Download logs: Click Save under Actions to export the current VMHA log data as a CSV file for offline analysis or support.





