Applicable Products
- QuTS hero h5.3.0 or later
- Virtualization Station 4.0 Beta or later
Introduction
VM High Availability (VMHA) is a feature in Virtualization Station that enables automatic failover of virtual machines between two QNAP NAS devices. It helps ensure service continuity in case of hardware failure by minimizing downtime.
This tutorial guides you through the complete setup process, including preparing your environment, creating a VMHA device pair, creating and managing VMHA groups, configuring failover, and troubleshooting common issues.
VMHA Requirements
System Requirements
| Component | Requirement |
|---|
| Operating system | QuTS hero h5.3.0 or later on both NAS devices. Note For best compatibility, it is recommended to use NAS devices that are running the same version of QuTS hero. |
| Processor | Both NAS devices must use CPUs from the same vendor (e.g., Intel® or AMD®). |
| Memory | The destination NAS must have enough memory to run the migrated virtual machines from the source NAS during failover. |
| Storage | Both NAS devices must have sufficient space for Virtualization Station to create a shared folder to store the VMHA disk images. Disk images must be stored on the NAS’s internal storage only, and external storage cannot be used. |
Network Requirements
| Component | Requirement |
|---|
| Network connections | At least two independent network connections are required between the two NAS devices.
These must be on different subnets: one for the management link and one for the availability link (used for data synchronization). |
| IP addresses | All interfaces used for HA must use static IPv4 addresses. IPv6 and VLAN settings must be disabled. |
| Firewall ports | If a firewall is in use, ensure that TCP ports 16500-16550 are open between the two NAS devices to allow HA communication.
For a complete list of service ports used by QNAP systems, see What network ports are used by QTS, QuTS hero, and QuTScloud systems. |
| Availability link | A network speed of at least 2.5 Gbps is strongly recommended, as link speed directly affects VM performance. For best performance, use a direct Ethernet connection between the NAS devices, avoiding switches when possible. |
| SSH service | The SSH service must be enabled on both NAS devices. For details, see Configuring SSH connections in the QuTS hero User Guide. |
Preconfiguration Requirements
- Configure compatible virtual switches on both NAS devices using Network & Virtual Switch. While the virtual switch names do not need to match, the interface assignments and network settings must be aligned. For details, see Virtual switch configuration in the QuTS hero User Guide.
- Ensure that both NAS devices are running the same version of QuTS hero. If the firmware versions differ, VMHA might not function as expected. To update the NAS firmware, see Firmware update in the QuTS hero User Guide.
- Configure both NAS devices to use the same NTP server for time synchronization. For details, see Configuring time settings in the QuTS hero User Guide.
- Ensure required ports are open or forwarded if using firewalls or NAT.
Warning
- VMHA cannot be enabled if either NAS is part of a Hero HA cluster. Ensure that both devices are in standalone mode by unpairing any existing Hero HA configuration before proceeding.
- Both NAS devices must run the same version of Virtualization Station. If the versions differ, such as after a system or app update, all HA protection groups will be paused automatically until version consistency is restored.
Procedure
Setting up virtual machine high availability (VMHA) involves three main steps to ensure that your virtual machines remain operational if the source NAS becomes unavailable.
- Create an HA Device Pair: Connect two NAS devices to form a high availability group. This step only pairs the two NAS devices, including verifying requirements, configuring the network connection for synchronization, and binding the virtual switches used by the VM. It does not include the future HA synchronization direction for the VMs.
- Create an HA Availability Group: Defines which virtual machine to protect, sets up the synchronization direction, and allocates storage on both NAS devices. This group manages the backup and recovery process for the VM.
- Configure the Failover Policy: Specifies the conditions that will automatically trigger failover, such as hardware issues or high resource usage.
Completing these steps ensures that selected virtual machines can be automatically restarted on the destination NAS in the event of a failure, minimizing service disruption.
Create an HA Device Pair
- Open Virtualization on the local NAS.
- Go to High Availability.
- Click Configure Paired Devices.
The Configure Paired Devices for VM Availability wizard opens. - Click Start.
- Review the requirements for paired devices.
- Click Next.
- Configure the local device settings.
Important
If you are using a direct physical connection (such as a dedicated Ethernet cable between the two NAS devices), do not select the adapters to configure the M-link (management link). Assigning an IP address in this scenario can cause Virtualization Station to report connection errors.
- Specify the IP address of the local device.
- Specify the device port number.
- Optional: Select Use SSL connection.
- Specify the device username.
- Specify the device password.
- Click Next.
- Configure the remote device settings.
- Specify the IP address of the remote device.
- Specify the device port number.
- Optional: Select Use SSL connection.
- Specify the device username.
- Specify the device password.
- Optional: Click Test.
Virtualization Station tests the local and remote device connection.
- Click Next.
The Configure Paired Devices and Their Credentials window appears.
- Review the local and remote device settings.
- Click Next.
The Configure Availability Link (A-Link) window appears.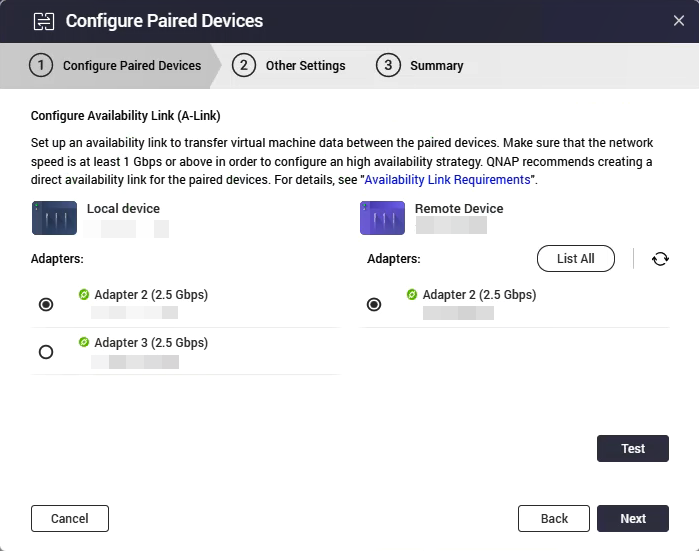
- Select the A-link adapters for the local and remote device.
Note
Click List All to view all the adapters linked to the local or remote device.
- Click Test.
Virtualization Station tests the A-link connectivity. - Click Next.
The Configure VM Network Settings window appears. - Configure the VM network settings for the paired devices.
- Click Add.
The Pairing VM Networks window appears.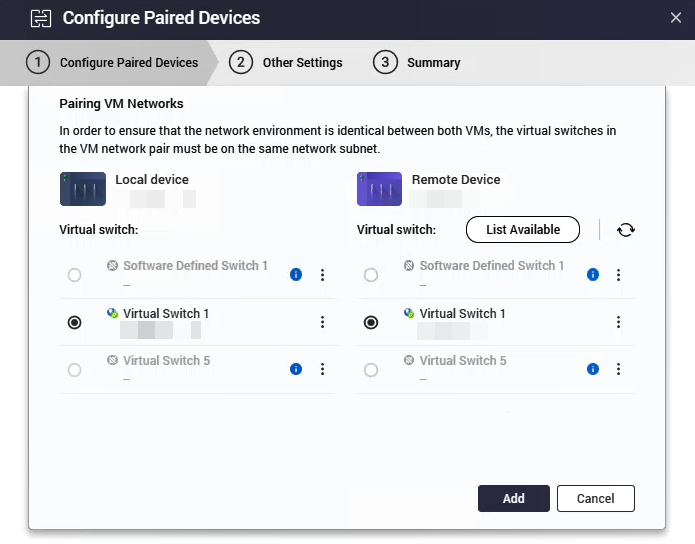
- Select the virtual switches for the local and remote devices.
Important
- The virtual switch or switches you select in this step determine which VMs can be protected by HA. Only VMs connected to the selected virtual switches will be available for selection.
- The wizard filters out incompatible virtual switches automatically. This includes switches that are not linked to a physical network adapter, reserved for system use (such as Docker or LXD), or configured with NAT or DHCP server functions.
If a virtual switch is missing from the list, review its settings in Network & Virtual Switch.
- Click Add.
Virtualization Station adds the virtual switches to the paired devices.
- Click Next.
The Other Settings window appears. - Configure the failover policy settings.
For details, see Configuring Failover Policy Settings. - Click Next.
- Review the settings.
- Click Finish.
Virtualization Station creates the HA device pair.
Tip
To manage the configured VMHA device pair, go to High Availability > Paired Devices.
- Go to Actions > Edit Paired Devices to update the configuration.
- Go to Actions > Unpair Paired Devices to remove the pairing.
Configure an HA Availability Group or Plan
Note
The Beta version of Virtualization Station 4.0 allows each NAS to create up to two HA availability groups, with each group limited to a single virtual machine.
- Log in to your local NAS.
- Open Virtualization Station.
- Next to Create Virtual Machine, click
 .
. - Click Create Availability Group.
The Availability Groups window appears. - Click Start.
The Create Availability Group window appears. - Select the synchronization direction.
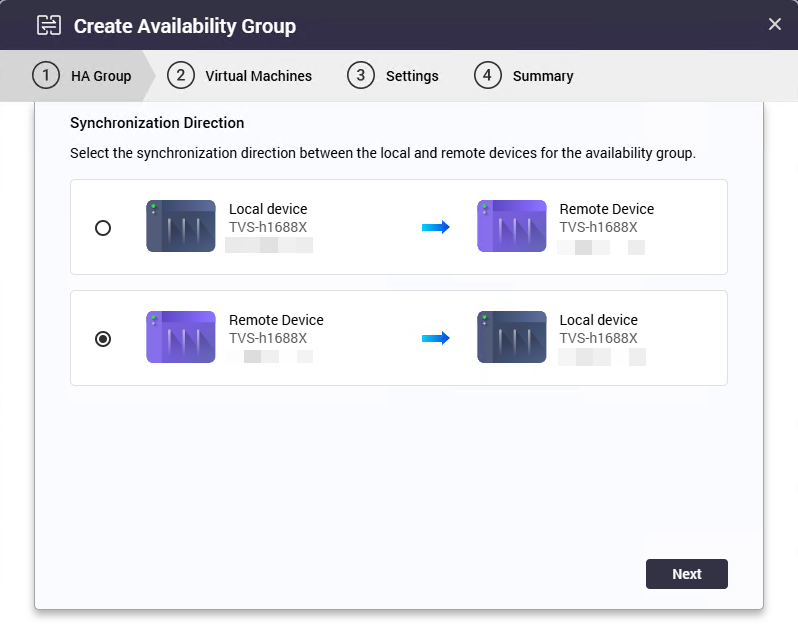
Note
The synchronization direction defines which NAS acts as the source and which NAS receives the VM data as a high-availability backup. The list of virtual machines displayed during the selection step depends on the chosen source NAS.
- Click Next.
- Configure the HA group settings.
- Specify an HA group name.
Note
A shared folder with the same name as the HA protection group is created in the selected storage pool on both the local and remote NAS devices. Ensure that the folder name is unique on each device to prevent naming conflicts.
Warning
Do not rename this folder for any VM that is already protected, as this may cause unexpected issues.
- Select the source device storage pool.
- Select the destination device storage pool.
- Specify the allocated quota for shared folder.
Note
Click Use Available Pool Capacity to automatically assign the smaller of the available capacities from the selected local and remote storage pools.
- Click Create.
The High Availability (HA) Group Configuration window appears. - Verify the configured group settings.
- Click Next.
The Virtual Machines window appears.
- Under the source device (local or remote device), click List Available.
- Select one or more virtual machines to include in the VMHA deployment.
- Click Next.
The Settings window opens. - Optional: Select Automatically resume the plan.
This option automatically restarts the HA plan after a reboot or interruption. - Click Next.
The Summary window opens. - Review the HA group settings.
- Click Create.
Virtualization Station creates the HA availability group.
Configure Failover Policy Settings
- Open Virtualization Station.
- Go to High Availability > Failover Policy.
- Configure the monitoring interval. This defines how frequently the system checks for failover conditions.
- Optional: Under Triggered Events, select the conditions that should trigger a failover. You can configure the following settings:
- Backup power mode: Initiates failover when the device runs on an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS).
- PSU redundancy loss: Initiates failover when the redundant power supply unit is disconnected or malfunctioning.
- System fan failure: Initiates failover when a system fan is not functioning properly.
- CPU load average exceeds threshold: Initiates failover when average CPU usage exceeds a defined percentage over a set duration.
- Memory load average exceeds threshold: Initiates failover when average memory usage exceeds a defined percentage over a set duration.
- Disk health error: Initiates failover when a virtual machine disk experiences a health issue or when a shared folder volume encounters an error.
- Network virtual switch error: Initiates failover when the virtual switch encounters a network-related error.
- Click Apply.
Virtualization Station saves and applies the failover policy settings to all the VMHA availability groups.
VMHA Monitoring, Troubleshooting, and Diagnostics
Monitor and Manage VMHA Groups
You can view the status of all VMHA groups, perform actions such as pause, resume, edit, or delete, and monitor synchronization progress and resource usage across both NAS devices.
Perform VMHA Actions
After an HA protection group is created, you can monitor and manage its status from the High Availability > Plans page.
- Open Virtualization Station.
- Go to High Availability > Plans.
- Under Action, click
 .
. - Identify a VMHA group or plan.
- Perform any of the following VMHA plan tasks.
| Task | Description |
|---|
| Switchover | Switches VMs between two NAS devices while keeping them online and operational, without requiring a reboot or suspension. |
| Pause | Temporarily suspends VMHA synchronization and failover protection for the HA group. |
| Delete | Removes the VMHA group and disables protection for the associated VM. |
| Resume | Restarts VMHA synchronization and failover monitoring for the group. |
| Edit | Opens the VMHA group settings for configuration changes. |
Note
If the Virtualization Station versions on the two NAS devices become inconsistent, a warning banner will appear on this page. All HA protection groups will be automatically paused until version consistency is restored.
Status Descriptions
| Status | Description |
|---|
Normal | The VMHA group is operating normally with no issues. |
Syncing | Initial or scheduled synchronization is in progress between the source and destination NAS. |
Pause | Synchronization is temporarily halted. The availability group is not actively syncing, but its configuration is preserved. Note This state can occur automatically if Virtualization Station is stopped or the NAS is shut down. |
Warning | VMHA protection is still active, but one or more issues may affect failover. Review and address the underlying causes promptly. |
Error | One or more critical failures have occurred. The VMHA group is no longer functioning correctly and requires immediate attention. |
Diagnose and Troubleshoot Common VMHA Conditions
To ensure stable and reliable HA operation, monitor system conditions and avoid configuration changes that may affect failover readiness.
Common Warning Conditions
| Warning | Description | Impact |
|---|
| Insufficient memory on the destination NAS | The available memory on the destination NAS is not enough to start the protected VM during a failover. | Failover will fail unless memory resources are increased or freed. |
| Degraded availability link | The availability link throughput has dropped below 50 Mbps or latency has exceeded 1 millisecond. | Reduced sync performance and increased recovery point objective (RPO). |
| Device pair configuration issues | Misconfigurations such as unstable management links or subnet mismatches between paired Virtual Switches. | Failover reliability may be compromised if not corrected. |
Warning
Do not modify or delete any virtual switch that is part of a VMHA pair. Changing or removing a paired virtual switch will result in a loss of network connectivity for the protected VM after failover and may cause the HA group to enter an error state.
Troubleshoot VMHA Group Issues
| Issue | Recommendation |
|---|
| Virtualization Station version mismatch | Ensure both NAS devices are running the same version of Virtualization Station. Check App Center for updates. Restart the app if needed. |
| Insufficient CPU or memory on source or destination NAS | Check system resource usage on both the source and destination NAS. Failover may fail if either system lacks sufficient CPU or memory to complete the process. Shut down unused VMs or services to free up resources. If necessary, consider upgrading the system memory. |
| Slow synchronization speeds or high latency | Use a direct network cable between NAS devices, or assign the availability link to a dedicated, high-speed subnet. |
| Virtual switch pairing errors | Open Network & Virtual Switch and confirm both switches are on the same subnet and have no conflicting settings (e.g., NAT or DHCP). |
| Cluster fails to create or join | Ensure both NAS devices are not already members of another Hero HA or VMHA cluster. Unpair any existing clusters before proceeding. |
Manage VMHA Logs
You can view and download VMHA-related logs to assist with troubleshooting, auditing, or verifying the system’s failover behavior. These logs provide detailed records of synchronization events, status changes, and system alerts, helping administrators diagnose issues and maintain operational visibility.
- Open Virtualization Station.
- Go to High Availability > Logs.
- Perform any of the following tasks.
- Search logs: Enter keywords in the search bar to filter log entries by event type, VM name, or timestamp.
- Download logs: Click Save under Actions to export the current VMHA log data as a CSV file for offline analysis or support.
Further Reading
ผลิตภัณฑ์ที่รองรับ
- QuTS hero h5.3.0 or later
- Virtualization Station 4.0 Beta or later
บทนำ
VM ความพร้อมใช้งานสูง (VMHA) เป็นคุณสมบัติใน Virtualization Station ที่ช่วยให้สามารถ การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด อัตโนมัติของเครื่องเสมือนระหว่างอุปกรณ์ QNAP NAS สองตัว ช่วยให้มั่นใจได้ถึงความต่อเนื่องของบริการในกรณีที่เกิดความล้มเหลวของฮาร์ดแวร์โดยลด Downtime
คู่มือการใช้งานนี้จะแนะนำคุณตลอดกระบวนการตั้งค่าอย่างครบถ้วน รวมถึงการเตรียมสภาพแวดล้อมของคุณ การสร้างคู่ VMHA การสร้างและจัดการกลุ่ม VMHA การกำหนดค่า การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด และการแก้ไขปัญหาทั่วไป
ข้อกำหนด VMHA
ข้อกำหนดของระบบ
| ส่วนประกอบ | ข้อกำหนด |
|---|
| ระบบปฏิบัติการ | QuTS hero h5.3.0 หรือใหม่กว่าบนอุปกรณ์ NAS ทั้งสองตัว หมายเหตุ เพื่อความเข้ากันได้ดีที่สุด ขอแนะนำให้ใช้อุปกรณ์ NAS ที่ใช้เวอร์ชันเดียวกันของ QuTS hero |
| โปรเซสเซอร์ | อุปกรณ์ NAS ทั้งสองตัวต้องใช้ CPU จากผู้ผลิตเดียวกัน (เช่น Intel® หรือ AMD®) |
| หน่วยความจำ | NAS ปลายทางต้องมีหน่วยความจำเพียงพอในการรันเครื่องเสมือนที่ย้ายมาจาก NAS ต้นทางในระหว่าง การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด |
| ที่เก็บข้อมูล | อุปกรณ์ NAS ทั้งสองตัวต้องมีพื้นที่เพียงพอสำหรับ Virtualization Station ในการสร้างโฟลเดอร์ที่ใช้ร่วมกันเพื่อจัดเก็บภาพดิสก์ VMHA ภาพดิสก์ต้องถูกจัดเก็บใน ที่เก็บข้อมูล ภายในของ NAS เท่านั้น และไม่สามารถใช้ ที่เก็บข้อมูล ภายนอกได้ |
ข้อกำหนดด้านเครือข่าย
| ส่วนประกอบ | ข้อกำหนด |
|---|
| การเชื่อมต่อเครือข่าย | ต้องมีการเชื่อมต่อเครือข่ายอิสระอย่างน้อยสองเส้นระหว่างอุปกรณ์ NAS ทั้งสองเครื่อง
ซึ่งต้องอยู่ในซับเน็ตที่แตกต่างกัน: หนึ่งสำหรับลิงก์การจัดการและอีกหนึ่งสำหรับลิงก์ความพร้อมใช้งาน (ใช้สำหรับการซิงโครไนซ์ข้อมูล) |
| ที่อยู่ IP | อินเทอร์เฟซทั้งหมดที่ใช้สำหรับ HA ต้องใช้ที่อยู่ IPv4 แบบคงที่ ต้องปิดการตั้งค่า IPv6 และ VLAN |
| ไฟร์วอลล์ พอร์ต | หากใช้ ไฟร์วอลล์ ให้ตรวจสอบว่าพอร์ต TCP 16500-16550 เปิดระหว่างอุปกรณ์ NAS ทั้งสองเครื่องเพื่อให้การสื่อสาร HA ทำงานได้
สำหรับรายการพอร์ตบริการทั้งหมดที่ใช้โดยระบบ QNAP ดูที่ พอร์ตเครือข่ายที่ใช้โดยระบบ QTS, QuTS hero และ QuTScloud |
| ลิงก์ความพร้อมใช้งาน | แนะนำให้ใช้ความเร็วเครือข่ายอย่างน้อย 2.5 Gbps เนื่องจากความเร็วลิงก์มีผลโดยตรงต่อประสิทธิภาพของ VM เพื่อประสิทธิภาพที่ดีที่สุด ควรใช้การเชื่อมต่อ Ethernet โดยตรงระหว่างอุปกรณ์ NAS หลีกเลี่ยงการใช้สวิตช์หากเป็นไปได้ |
| บริการ SSH | ต้องเปิดใช้งานบริการ SSH บนอุปกรณ์ NAS ทั้งสองเครื่อง สำหรับรายละเอียด ดูที่ การตั้งค่าการเชื่อมต่อ SSH ใน คู่มือผู้ใช้ QuTS hero |
ข้อกำหนดก่อนการกำหนดค่า
- กำหนดค่าสวิตช์เสมือนที่เข้ากันได้บนอุปกรณ์ NAS ทั้งสองเครื่องโดยใช้ เครือข่ายและสวิตช์เสมือน แม้ว่าชื่อสวิตช์เสมือนจะไม่จำเป็นต้องตรงกัน แต่การกำหนดค่าอินเทอร์เฟซและการตั้งค่าเครือข่ายต้องสอดคล้องกัน สำหรับรายละเอียด ดูที่ การตั้งค่า Virtual switch ใน คู่มือผู้ใช้ QuTS hero
- ตรวจสอบให้อุปกรณ์ NAS ทั้งสองเครื่องใช้เวอร์ชันเดียวกันของ QuTS hero หากเวอร์ชัน เฟิร์มแวร์ แตกต่างกัน VMHA อาจไม่ทำงานตามที่คาดหวัง ในการอัปเดต เฟิร์มแวร์ ของ NAS ดูที่ อัปเดตเฟิร์มแวร์ ใน คู่มือผู้ใช้ QuTS hero
- กำหนดค่าให้อุปกรณ์ NAS ทั้งสองเครื่องใช้เซิร์ฟเวอร์ NTP เดียวกันสำหรับการซิงโครไนซ์เวลา สำหรับรายละเอียด ดูที่ การตั้งค่าเวลา ใน คู่มือผู้ใช้ QuTS hero
- ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าพอร์ตที่จำเป็นเปิดหรือส่งต่อหากใช้ ไฟร์วอลล์ หรือ NAT
คำเตือน
- ไม่สามารถเปิดใช้งาน VMHA ได้หาก NAS ใด ๆ เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของ Hero HA คลัสเตอร์ ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าอุปกรณ์ทั้งสองอยู่ในโหมดสแตนด์อโลนโดยยกเลิกการจับคู่การตั้งค่า Hero HA ที่มีอยู่ก่อนดำเนินการต่อ
- อุปกรณ์ NAS ทั้งสองต้องใช้เวอร์ชันเดียวกันของ Virtualization Station หากเวอร์ชันต่างกัน เช่น หลังจากการอัปเดตระบบหรือแอป กลุ่มการป้องกัน HA ทั้งหมดจะถูกหยุดชั่วคราวโดยอัตโนมัติจนกว่าจะคืนความสอดคล้องของเวอร์ชัน
ขั้นตอน
การตั้งค่า ความพร้อมใช้งานสูง เครื่องเสมือน (VMHA) ประกอบด้วยสามขั้นตอนหลักเพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าเครื่องเสมือนของคุณยังคงทำงานได้หาก NAS ต้นทางไม่สามารถใช้งานได้
- สร้างคู่เครื่อง HA: เชื่อมต่ออุปกรณ์ NAS สองเครื่องเพื่อสร้างกลุ่ม ความพร้อมใช้งานสูง ขั้นตอนนี้เพียงจับคู่ NAS สองเครื่อง รวมถึงการตรวจสอบข้อกำหนด การกำหนดค่าเครือข่ายสำหรับการซิงโครไนซ์ และการผูกสวิตช์เสมือนที่ใช้โดย VM ไม่รวมทิศทางการซิงโครไนซ์ HA ในอนาคตสำหรับ VM
- สร้างกลุ่มความพร้อมใช้งาน HA: กำหนดว่าเครื่องเสมือนใดที่จะป้องกัน ตั้งค่าทิศทางการซิงโครไนซ์ และจัดสรร ที่เก็บข้อมูล บนอุปกรณ์ NAS ทั้งสองเครื่อง กลุ่มนี้จัดการกระบวนการสำรองและกู้คืนสำหรับ VM
- กำหนดนโยบาย Failover: ระบุเงื่อนไขที่จะกระตุ้น การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด โดยอัตโนมัติ เช่น ปัญหาฮาร์ดแวร์หรือการใช้งานทรัพยากรสูง
การทำตามขั้นตอนเหล่านี้จะช่วยให้เครื่องเสมือนที่เลือกสามารถรีสตาร์ทอัตโนมัติบน NAS ปลายทางในกรณีที่เกิดความล้มเหลว ลดการหยุดชะงักของบริการ
สร้างคู่อุปกรณ์ HA
- เปิดการจำลองเสมือนบน NAS ท้องถิ่น
- ไปที่ ความพร้อมใช้งานสูง
- คลิก กำหนดค่าอุปกรณ์ที่จับคู่.
วิซาร์ด กำหนดค่าอุปกรณ์ที่จับคู่สำหรับความพร้อมใช้งานของ VM จะเปิดขึ้น - คลิก เริ่มต้น
- ตรวจสอบข้อกำหนดสำหรับอุปกรณ์ที่จับคู่
- คลิก ถัดไป
- กำหนดค่าการตั้งค่าอุปกรณ์ท้องถิ่น
สำคัญ
หากคุณใช้การเชื่อมต่อทางกายภาพโดยตรง (เช่น สาย Ethernet เฉพาะระหว่างอุปกรณ์ NAS สองเครื่อง) อย่าเลือกอะแดปเตอร์เพื่อกำหนดค่า M-link (ลิงก์การจัดการ) การกำหนดที่อยู่ IP ในสถานการณ์นี้อาจทำให้ Virtualization Station รายงานข้อผิดพลาดการเชื่อมต่อ
- ระบุที่อยู่ IP ของอุปกรณ์ท้องถิ่น
- ระบุหมายเลขพอร์ตของอุปกรณ์
- ตัวเลือก: เลือก ใช้การเชื่อมต่อ SSL
- ระบุชื่อผู้ใช้ของอุปกรณ์
- ระบุรหัสผ่านของอุปกรณ์
- คลิก ถัดไป
- กำหนดค่าการตั้งค่าอุปกรณ์ระยะไกล
- ระบุที่อยู่ IP ของอุปกรณ์ระยะไกล
- ระบุหมายเลขพอร์ตของอุปกรณ์
- ตัวเลือก: เลือก ใช้การเชื่อมต่อ SSL
- ระบุชื่อผู้ใช้ของอุปกรณ์
- ระบุรหัสผ่านของอุปกรณ์
- ตัวเลือก: คลิก ทดสอบ.
Virtualization Station ทดสอบการเชื่อมต่ออุปกรณ์ในเครื่องและระยะไกล
- คลิก ถัดไป.
หน้าต่าง กำหนดค่าอุปกรณ์ที่จับคู่และข้อมูลรับรอง ปรากฏขึ้น
- ตรวจสอบการตั้งค่าอุปกรณ์ในเครื่องและระยะไกล
- คลิก ถัดไป.
หน้าต่าง กำหนดค่าลิงก์ความพร้อมใช้งาน (A-Link) ปรากฏขึ้น
- เลือกอะแดปเตอร์ A-link สำหรับอุปกรณ์ในเครื่องและระยะไกล
หมายเหตุ
คลิก แสดงทั้งหมด เพื่อดูอะแดปเตอร์ทั้งหมดที่เชื่อมโยงกับอุปกรณ์ในเครื่องหรือระยะไกล
- คลิก ทดสอบ.
Virtualization Station ทดสอบการเชื่อมต่อ A-link - คลิก ถัดไป.
หน้าต่าง กำหนดค่าเครือข่าย VM ปรากฏขึ้น - กำหนดค่าเครือข่าย VM สำหรับอุปกรณ์ที่จับคู่
- คลิก เพิ่ม.
หน้าต่าง จับคู่เครือข่าย VM ปรากฏขึ้น
- เลือกสวิตช์เสมือนสำหรับอุปกรณ์ในเครื่องและระยะไกล
สำคัญ
- สวิตช์เสมือนที่คุณเลือกในขั้นตอนนี้จะกำหนดว่า VM ใดสามารถได้รับการปกป้องโดย HA ได้ เฉพาะ VM ที่เชื่อมต่อกับสวิตช์เสมือนที่เลือกเท่านั้นที่จะสามารถเลือกได้
- วิซาร์ดจะกรองสวิตช์เสมือนที่ไม่เข้ากันโดยอัตโนมัติ ซึ่งรวมถึงสวิตช์ที่ไม่ได้เชื่อมโยงกับอะแดปเตอร์เครือข่ายทางกายภาพ สงวนไว้สำหรับการใช้งานระบบ (เช่น Docker หรือ LXD) หรือกำหนดค่าด้วยฟังก์ชัน NAT หรือ DHCP server
หากสวิตช์เสมือนหายไปจากรายการ ให้ตรวจสอบการตั้งค่าใน เครือข่ายและสวิตช์เสมือน
- คลิก เพิ่ม.
Virtualization Station เพิ่มสวิตช์เสมือนให้กับอุปกรณ์ที่จับคู่
- คลิก ถัดไป.
หน้าต่าง การตั้งค่าอื่นๆ ปรากฏขึ้น - กำหนดค่าการตั้งค่านโยบาย การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด
สำหรับรายละเอียด ดูที่ การตั้งค่านโยบาย Failover - คลิก ถัดไป
- ตรวจสอบการตั้งค่า
- คลิก เสร็จสิ้น
Virtualization Station สร้างคู่ของอุปกรณ์ HA
เคล็ดลับ
เพื่อจัดการคู่ของอุปกรณ์ VMHA ที่กำหนดค่าแล้ว ไปที่ ความพร้อมใช้งานสูง >อุปกรณ์ที่จับคู่
- ไปที่ การดำเนินการ >แก้ไขอุปกรณ์ที่จับคู่ เพื่ออัปเดตการกำหนดค่า
- ไปที่ การดำเนินการ >ยกเลิกการจับคู่ของอุปกรณ์ เพื่อลบการจับคู่
กำหนดค่ากลุ่มหรือแผนความพร้อมใช้งาน HA
หมายเหตุ
เวอร์ชัน Beta ของ Virtualization Station 4.0 อนุญาตให้แต่ละ NAS สร้างกลุ่มความพร้อมใช้งาน HA ได้สูงสุดสองกลุ่ม โดยแต่ละกลุ่มจำกัดเพียงเครื่องเสมือนเดียว
- เข้าสู่ระบบ NAS ในพื้นที่ของคุณ
- เปิด Virtualization Station
- ถัดจาก สร้างเครื่องเสมือน คลิก

- คลิก สร้างกลุ่มความพร้อมใช้งาน.
หน้าต่างกลุ่มความพร้อมใช้งานปรากฏขึ้น - คลิก เริ่ม.
หน้าต่าง สร้างกลุ่มความพร้อมใช้งาน ปรากฏขึ้น - เลือกทิศทางการซิงโครไนซ์

หมายเหตุ
ทิศทางการซิงโครไนซ์กำหนดว่า NAS ใดทำหน้าที่เป็นแหล่งที่มาและ NAS ใดรับข้อมูล VM เป็นการสำรองข้อมูลความพร้อมใช้งานสูง รายการเครื่องเสมือนที่แสดงในขั้นตอนการเลือกขึ้นอยู่กับ NAS แหล่งที่มา
- คลิก ถัดไป
- กำหนดค่าการตั้งค่ากลุ่ม HA
- ระบุชื่อกลุ่ม HA
หมายเหตุ
โฟลเดอร์ที่ใช้ร่วมกันที่มีชื่อเดียวกับกลุ่มการป้องกัน HA จะถูกสร้างขึ้นใน ที่เก็บข้อมูล pool ที่เลือกบนอุปกรณ์ NAS ทั้งในพื้นที่และระยะไกล ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าโฟลเดอร์มีชื่อที่ไม่ซ้ำกันในแต่ละอุปกรณ์เพื่อป้องกันความขัดแย้งของชื่อ
คำเตือน
อย่าเปลี่ยนชื่อโฟลเดอร์นี้สำหรับ VM ใด ๆ ที่ได้รับการป้องกันแล้ว เนื่องจากอาจทำให้เกิดปัญหาที่ไม่คาดคิด
- เลือกพูล ที่เก็บข้อมูล ของอุปกรณ์ต้นทาง
- เลือกพูล ที่เก็บข้อมูล ของอุปกรณ์ปลายทาง
- ระบุโควต้าที่จัดสรรสำหรับโฟลเดอร์ที่แชร์
หมายเหตุ
คลิก ใช้ความจุพูลที่มีอยู่ เพื่อกำหนดความจุที่เล็กกว่าจากพูล ที่เก็บข้อมูล ที่เลือกทั้งในเครื่องและระยะไกลโดยอัตโนมัติ
- คลิก สร้าง.
หน้าต่าง ความพร้อมใช้งานสูง (HA) การตั้งค่ากลุ่ม ปรากฏขึ้น - ตรวจสอบการตั้งค่ากลุ่มที่กำหนดค่าแล้ว
- คลิก ถัดไป.
หน้าต่าง เครื่องเสมือน ปรากฏขึ้น
- ภายใต้อุปกรณ์ต้นทาง (อุปกรณ์ในเครื่องหรือระยะไกล) คลิก รายการที่มีอยู่
- เลือกเครื่องเสมือนหนึ่งเครื่องหรือมากกว่าเพื่อรวมในการปรับใช้ VMHA
- คลิก ถัดไป.
หน้าต่าง การตั้งค่า เปิดขึ้น - ตัวเลือก: เลือก ดำเนินการแผนต่อโดยอัตโนมัติ.
ตัวเลือกนี้จะเริ่มแผน HA ใหม่โดยอัตโนมัติหลังจากรีบูตหรือหยุดชะงัก - คลิก ถัดไป.
หน้าต่าง สรุป เปิดขึ้น - ตรวจสอบการตั้งค่ากลุ่ม HA
- คลิก สร้าง.
Virtualization Station สร้างกลุ่มความพร้อมใช้งาน HA
กำหนดค่า การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด การตั้งค่านโยบาย
- เปิด Virtualization Station
- ไปที่ ความพร้อมใช้งานสูง >การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด นโยบาย
- กำหนดช่วงเวลาการตรวจสอบ ซึ่งจะกำหนดความถี่ที่ระบบตรวจสอบเงื่อนไข การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด
- ตัวเลือก: ภายใต้ เหตุการณ์ที่ถูกกระตุ้น, เลือกเงื่อนไขที่ควรกระตุ้น การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด คุณสามารถกำหนดค่าการตั้งค่าต่อไปนี้:
- โหมดพลังงานสำรอง: เริ่ม การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด เมื่ออุปกรณ์ทำงานบนแหล่งจ่ายไฟสำรอง (UPS)
- การสูญเสียความซ้ำซ้อนของ PSU: เริ่ม การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด เมื่อหน่วยจ่ายไฟสำรองถูกตัดการเชื่อมต่อหรือทำงานผิดปกติ
- ความล้มเหลวของพัดลมระบบ: เริ่ม การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด เมื่อพัดลมระบบไม่ทำงานอย่างถูกต้อง
- ค่าเฉลี่ยโหลด CPU เกินเกณฑ์: เริ่ม การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด เมื่อการใช้งาน CPU เฉลี่ยเกินเปอร์เซ็นต์ที่กำหนดในช่วงเวลาที่กำหนด
- ค่าเฉลี่ยโหลดหน่วยความจำเกินเกณฑ์: เริ่ม การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด เมื่อการใช้งานหน่วยความจำเฉลี่ยเกินเปอร์เซ็นต์ที่กำหนดในช่วงเวลาที่กำหนด
- ข้อผิดพลาดสุขภาพดิสก์: เริ่มต้น การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด เมื่อดิสก์ของเครื่องเสมือนมีปัญหาด้านสุขภาพหรือเมื่อโวลุ่มของโฟลเดอร์ที่แชร์เกิดข้อผิดพลาด
- ข้อผิดพลาดของสวิตช์เครือข่ายเสมือน: เริ่มต้น การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด เมื่อสวิตช์เสมือนพบข้อผิดพลาดที่เกี่ยวข้องกับเครือข่าย
- คลิก Apply.
Virtualization Station บันทึกและใช้การตั้งค่านโยบาย การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด กับกลุ่มความพร้อมใช้งาน VMHA ทั้งหมด
การตรวจสอบ การแก้ไขปัญหา และการวินิจฉัย VMHA
ตรวจสอบและจัดการกลุ่ม VMHA
คุณสามารถดูสถานะของกลุ่ม VMHA ทั้งหมด ดำเนินการต่างๆ เช่น หยุดชั่วคราว ดำเนินการต่อ แก้ไข หรือลบ และตรวจสอบความคืบหน้าของการซิงโครไนซ์และการใช้งานทรัพยากรในอุปกรณ์ NAS ทั้งสองเครื่อง
ดำเนินการ VMHA
หลังจากสร้างกลุ่มการป้องกัน HA แล้ว คุณสามารถตรวจสอบและจัดการสถานะของมันได้จากหน้า ความพร้อมใช้งานสูง > Plans
- เปิด Virtualization Station
- ไปที่ ความพร้อมใช้งานสูง >Plans
- ภายใต้ การกระทำ, คลิก

- ระบุกลุ่มหรือแผน VMHA
- ดำเนินการงานแผน VMHA ใดๆ ต่อไปนี้
| งาน | คำอธิบาย |
|---|
| สลับ | สลับเครื่องเสมือนระหว่างอุปกรณ์ NAS สองเครื่องในขณะที่ยังคงออนไลน์และทำงานได้ โดยไม่ต้องรีบูตหรือหยุดชั่วคราว |
| หยุดชั่วคราว | หยุดการซิงโครไนซ์ VMHA และการป้องกัน การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด ชั่วคราวสำหรับกลุ่ม HA |
| ลบ | ลบกลุ่ม VMHA และปิดการป้องกันสำหรับเครื่องเสมือนที่เกี่ยวข้อง |
| ดำเนินการต่อ | เริ่มการซิงโครไนซ์ VMHA และการตรวจสอบ การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด สำหรับกลุ่มอีกครั้ง |
| แก้ไข | เปิดการตั้งค่ากลุ่ม VMHA เพื่อเปลี่ยนแปลงการกำหนดค่า |
หมายเหตุ
หากเวอร์ชัน Virtualization Station บนอุปกรณ์ NAS สองเครื่องไม่สอดคล้องกัน แบนเนอร์เตือนจะปรากฏบนหน้านี้ กลุ่มการป้องกัน HA ทั้งหมดจะถูกหยุดชั่วคราวโดยอัตโนมัติจนกว่าจะคืนความสอดคล้องของเวอร์ชัน
คำอธิบายสถานะ
| สถานะ | คำอธิบาย |
|---|
ปกติ | กลุ่ม VMHA ทำงานตามปกติไม่มีปัญหา |
กำลังซิงค์ | การซิงโครไนซ์เริ่มต้นหรือที่กำหนดเวลาไว้กำลังดำเนินการระหว่าง NAS ต้นทางและปลายทาง |
หยุดชั่วคราว | การซิงโครไนซ์ถูกหยุดชั่วคราวชั่วคราว กลุ่มความพร้อมใช้งานไม่ได้ซิงค์อยู่ แต่การกำหนดค่าของมันยังคงอยู่ หมายเหตุ สถานะนี้สามารถเกิดขึ้นได้โดยอัตโนมัติหาก Virtualization Station ถูกหยุดหรือ NAS ถูกปิด |
คำเตือน | การป้องกัน VMHA ยังคงใช้งานอยู่ แต่มีปัญหาหนึ่งหรือมากกว่าที่อาจส่งผลต่อ การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด ตรวจสอบและแก้ไขสาเหตุที่แท้จริงโดยเร็ว |
ข้อผิดพลาด | เกิดความล้มเหลวที่สำคัญหนึ่งหรือมากกว่า กลุ่ม VMHA ไม่ทำงานอย่างถูกต้องและต้องการการดูแลทันที |
วินิจฉัยและแก้ไขปัญหาสภาพ VMHA ทั่วไป
เพื่อให้การทำงานของ HA มีเสถียรภาพและเชื่อถือได้ ตรวจสอบสภาพระบบและหลีกเลี่ยงการเปลี่ยนแปลงการกำหนดค่าที่อาจส่งผลต่อความพร้อมของ การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด
สภาพคำเตือนทั่วไป
| คำเตือน | คำอธิบาย | ผลกระทบ |
|---|
| หน่วยความจำไม่เพียงพอใน NAS ปลายทาง | หน่วยความจำที่มีอยู่บน NAS ปลายทางไม่เพียงพอที่จะเริ่ม VM ที่ได้รับการปกป้องในระหว่าง การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด | การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด จะล้มเหลวหากไม่เพิ่มหรือปล่อยทรัพยากรหน่วยความจำ |
| ลิงก์ความพร้อมใช้งานที่ลดลง | ลิงก์ความพร้อมใช้งาน อัตราความเร็ว ลดลงต่ำกว่า 50 Mbps หรือค่าความหน่วงเกิน 1 มิลลิวินาที | ประสิทธิภาพการซิงค์ลดลงและเป้าหมายจุดกู้คืน (RPO) เพิ่มขึ้น |
| ปัญหาการกำหนดค่าคู่ของอุปกรณ์ | การกำหนดค่าผิดพลาด เช่น ลิงก์การจัดการที่ไม่เสถียรหรือการไม่ตรงกันของซับเน็ตระหว่าง Virtual Switches ที่จับคู่ | ความน่าเชื่อถือของ การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด อาจถูกทำลายหากไม่แก้ไข |
คำเตือน
อย่าแก้ไขหรือลบ Virtual Switch ใดๆ ที่เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของคู่ VMHA การเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือลบ Virtual Switch ที่จับคู่จะทำให้การเชื่อมต่อเครือข่ายของ VM ที่ได้รับการปกป้องสูญหายหลังจาก การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด และอาจทำให้กลุ่ม HA เข้าสู่สถานะข้อผิดพลาด
แก้ไขปัญหากลุ่ม VMHA
| ปัญหา | คำแนะนำ |
|---|
| เวอร์ชัน Virtualization Station ไม่ตรงกัน | ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าอุปกรณ์ NAS ทั้งสองเครื่องใช้เวอร์ชันเดียวกันของ Virtualization Station ตรวจสอบ App Center สำหรับการอัปเดต รีสตาร์ทแอปหากจำเป็น |
| CPU หรือหน่วยความจำไม่เพียงพอบน NAS ต้นทางหรือปลายทาง | ตรวจสอบการใช้งานทรัพยากรระบบบน NAS ต้นทางและปลายทาง การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด อาจล้มเหลวหากระบบใดระบบหนึ่งขาด CPU หรือหน่วยความจำเพียงพอที่จะดำเนินการให้เสร็จสิ้น ปิด VM หรือบริการที่ไม่ได้ใช้งานเพื่อปล่อยทรัพยากร หากจำเป็นให้พิจารณาอัปเกรดหน่วยความจำระบบ |
| ความเร็วในการซิงโครไนซ์ช้าหรือค่าความหน่วงสูง | ใช้สายเคเบิลเครือข่ายโดยตรงระหว่างอุปกรณ์ NAS หรือกำหนดลิงก์ความพร้อมใช้งานไปยังซับเน็ตความเร็วสูงที่เฉพาะเจาะจง |
| ข้อผิดพลาดในการจับคู่ Virtual Switch | เปิด เครือข่ายและสวิตช์เสมือน และยืนยันว่า Switch ทั้งสองอยู่ในซับเน็ตเดียวกันและไม่มีการตั้งค่าที่ขัดแย้งกัน (เช่น NAT หรือ DHCP) |
| คลัสเตอร์ ล้มเหลวในการสร้างหรือเข้าร่วม | ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าอุปกรณ์ NAS ทั้งสองเครื่องไม่ได้เป็นสมาชิกของ Hero HA หรือ VMHA คลัสเตอร์ อื่นๆ อยู่แล้ว ยกเลิกการจับคู่ คลัสเตอร์ ที่มีอยู่ก่อนดำเนินการต่อ |
จัดการบันทึก VMHA
คุณสามารถดูและดาวน์โหลดบันทึกที่เกี่ยวข้องกับ VMHA เพื่อช่วยในการแก้ไขปัญหา การตรวจสอบ หรือการยืนยันพฤติกรรม การย้ายโหนดเมื่อเกิดข้อผิดพลาด ของระบบ บันทึกเหล่านี้ให้บันทึกเหตุการณ์การซิงโครไนซ์ การเปลี่ยนแปลงสถานะ และการแจ้งเตือนของระบบอย่างละเอียด ช่วยให้ ผู้ดูแลระบบ วินิจฉัยปัญหาและรักษาการมองเห็นการดำเนินงาน
- เปิด Virtualization Station
- ไปที่ ความพร้อมใช้งานสูง >บันทึก.
- ดำเนินการตามงานต่อไปนี้.
- ค้นหาบันทึก: ป้อนคำหลักในแถบค้นหาเพื่อกรองรายการบันทึกตามประเภทเหตุการณ์ ชื่อ VM หรือเวลาที่บันทึก.
- ดาวน์โหลดบันทึก: คลิก บันทึก ใต้ การดำเนินการ เพื่อส่งออกข้อมูลบันทึก VMHA ปัจจุบันเป็นไฟล์ CSV สำหรับการวิเคราะห์แบบออฟไลน์หรือการสนับสนุน.
อ่านเพิ่มเติม





 หมายเหตุ
หมายเหตุ






