How to Optimize Memory Usage to Enhance Device & Virtual Machine Performance
Introduction
A lack of system memory affects both system & virtual machine performance (VM). To remedy this, Virtualization Station offers a Memory Optimizer feature that combines memory sharing and dynamic memory allocation to ensure memory usage on the device is used effectively. In this tutorial, we will explain how to optimize the memory usage to enhance flexibility and scalability for system and virtual machines.
Environment Setup
This tutorial uses the following hardware environment, but the steps should be largely identical regardless of your specific setup.
|
Device |
Type |
|---|---|
|
Host Device |
TS-677-1600-8G |
|
VM1 |
Windows 10 64-bit (4 cores / 4 GB) |
|
VM2 |
Windows 10 64-bit (4 cores / 4 GB) |
|
VM3 |
Ubuntu 18.04 64-bit (4 cores / 2 GB) |
|
VM4 |
Ubuntu 18.04 64-bit (4 cores / 2 GB) |
Preferences and Settings Configuration
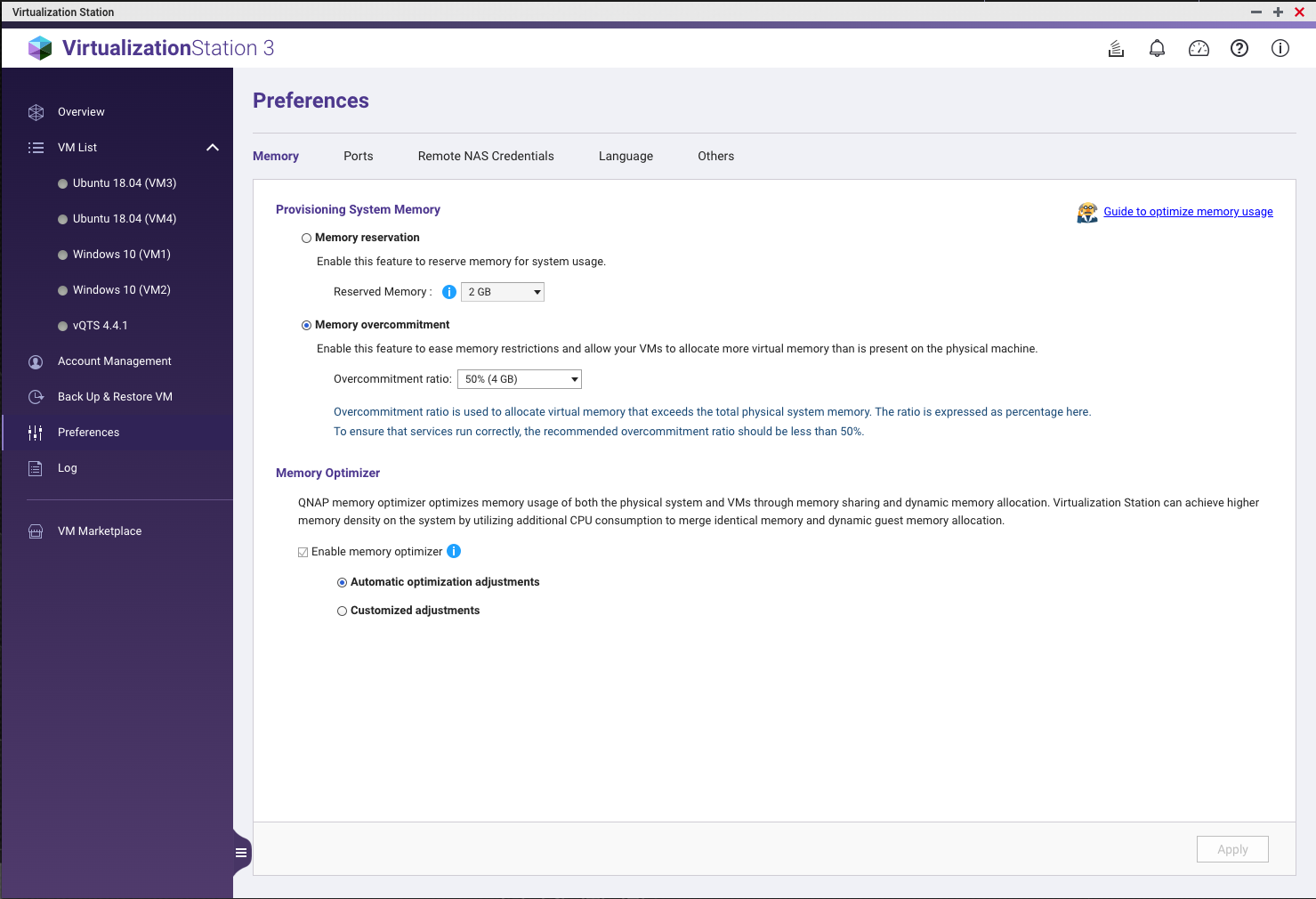
Configuring Memory Overcommitment and Memory Optimizer
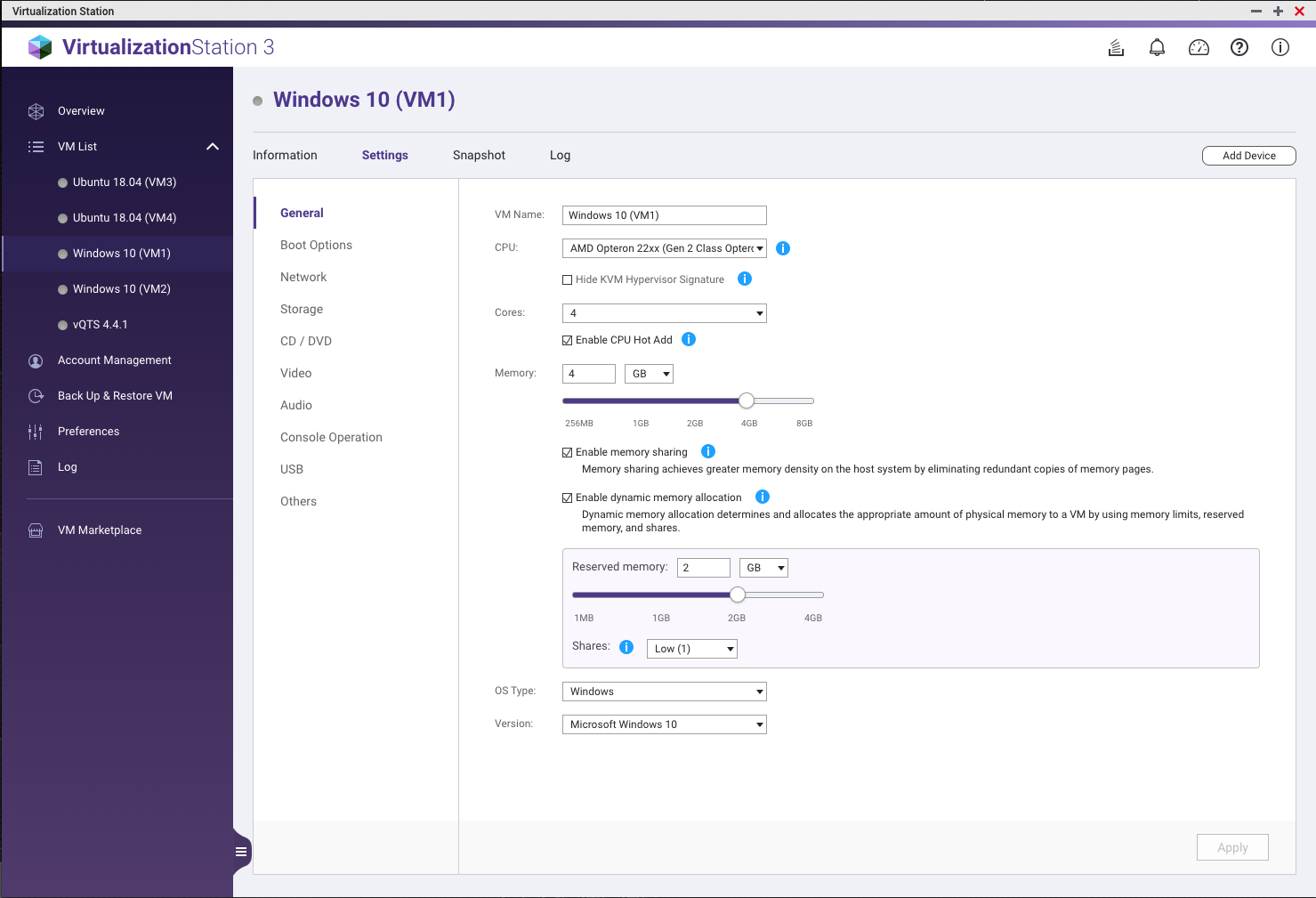
Configuring Memory Sharing and Dynamic Memory Allocation
You must complete this process for each virtual machine.
Installing the VirtIO Balloon Driver on Virtual Machines
Modern Linux-based virtual machines (VM3 & VM4) include the Balloon drivers by default. This process is only required for Windows-based virtual machines (VM1 & VM2).
- Start Virtualization Station.
- Identify a VM.
- Stop the VM.
- Go to VM Information.
- Insert the Guest Tools CD ISO file.
- Start the VM.
- Click
 to open the VM console.
to open the VM console. - Navigate to the CD Drive.
- Install qnap-guest-tools from the Guest Tools CD.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to install QNAP Guest Tools.
Configuring Auto Start
This step is optional, but may help reduce issues with insufficient memory during VM startup. Because Windows-based virtual machines use all allocated memory when starting, QNAP recommends starting these VMs first.
You must complete this process for each virtual machine.
Review
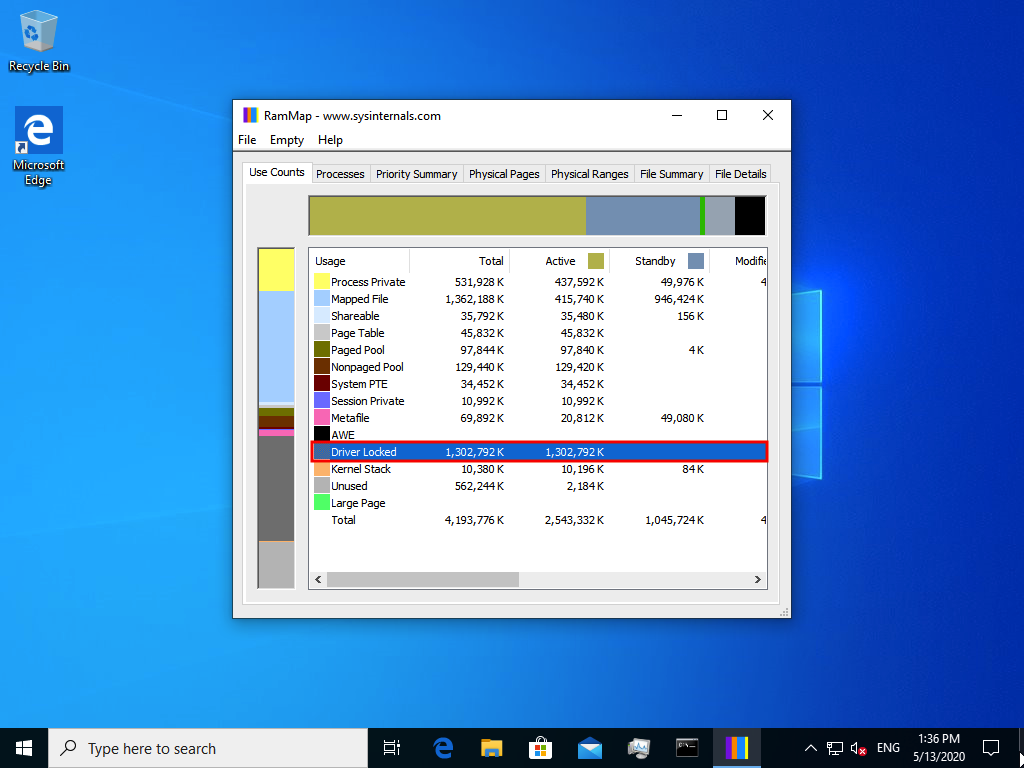
Checking Memory Sharing
Checking Dynamic Memory Allocation on Windows VMs
These directions only apply to Windows-based virtual machines.
Checking Dynamic Memory Allocation on Linux VMs
These directions only apply to Linux-based virtual machines.

 .
.