How to debug and fix common container issues in Container Station?
Container Station enables you to deploy third-party applications and containers on your QNAP device. Open-source images used to create these containers may introduce deployment issues.
QNAP does not provide technical support for third-party images. Follow these steps to diagnose and resolve common container-related issues.
Checking container configuration
Containers inherit all attributes of the source image. Scan the image file to identify security vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and backdoor threats before deployment.
If the container encounters issues after deployment, analyze the container logs to diagnose and resolve problems.
Examining image information
Review the image prerequisites and complete any required steps before deploying the container.
For example, deploying a PostgreSQL container using the postgres image requires setting the POSTGRES_PASSWORD environment variable. The container fails to deploy without this variable.
POSTGRES_PASSWORD environment variable in the Environment section.Analyzing Container Station event logs
Container Station logs all application and container activity. Failure logs provide explicit error messages, including the application or container name, error code, and error details.
- Open Container Station.
- Click Event Logs.
- Locate failure logs.
Example 1
In this example, the event log recorded a startup failure because the specified ports were already in use by other services, preventing the container from binding to the required network interfaces.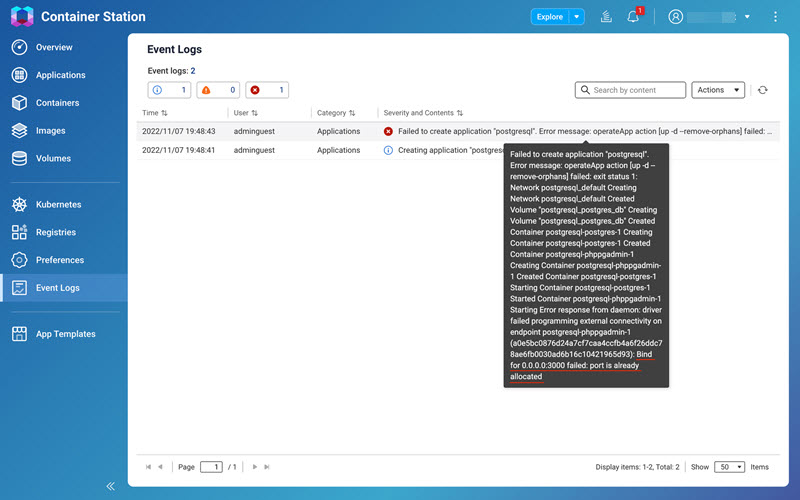
Example 2
The event log recorded a startup failure in this example due to a misconfigured entrypoint command, which prevented the container from executing the intended process.
Checking individual container logs
Analyze individual container logs for error and warning messages. Container Station logs detailed error states, such as missing environment variables, invalid naming formats, failed image retrievals, and initialization failures.
- Open Container Station.
- Click Containers.
- Select a container to open the details page.
- Click Logs.
- Review error and warning messages.
Example 1
The event log recorded a startup failure because the MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD environment variable was not set before deploying the MySQL container, causing it to exit immediately after initialization.
Example 2
The event log recorded a startup failure because the Rancher container was deployed using the rancher/rancher image without enabling privileged mode. Without the --privileged flag, the container could not initialize properly.
Verifying image compatibility
Ensure that the image is compatible with the processor architecture and operating system of your QNAP device. Incorrect image versions or architectures prevent containers from running.
Checking platform compatibility
Verify that the image platform matches your QNAP device’s CPU architecture. If transferring an image from another QNAP device, confirm that both devices use the same architecture.
Docker
The Docker image page provides a list of supported architectures and operating systems for each image version. The following are the general compatibility guidelines for Docker images:
linux/arm/v7images support 32-bit ARM architectures.linux/arm64/v8images support 64-bit ARM architectures.linux/amd64images support 64-bit x86 architectures.
LXD
For compatibility details, visit LXD Image Server. The following are the general architecture compatibility guidelines for LXD containers:
armhfcontainers support 32-bit ARM architectures.arm64containers support 64-bit ARM architectures.amd64containers support 64-bit x86 architectures.
Identifying container incompatibility
Incompatible Docker containers may log an exec format error, indicating an architecture mismatch.
When deploying incompatible LXD containers, Container Station records failure logs in the Event Logs page.
Checking page size compatibility
QNAP updated the system page size from 4K to 32K for improved performance on specific 32-bit ARM devices. This change may limit container access to memory resources, causing segmentation faults. Verify third-party container compatibility before deployment.
| Series | Models |
|---|---|
| TS-x31P | TS-531P |
| TS-x31P3 | TS-231P3, TS-431P3 |
| TS-x31X | TS-231X, TS-431X, TS-531X, TS-831X, TS-431X2, TS-431X3 |
| TS-x31KX | TS-431KX |
| TS-x31XU | TS-431XU, TS-431XU-RP, TS-831XU, TS-831XU-RP, TS-1231XU, TS-1231XU-RP |
| TS-x31XeU | TS-431XeU |
| TS-x35 | TS-1635 |
Checking the QNAP system configuration
Ensure that the QNAP device is properly configured for container deployment and orchestration.
Verifying network settings
- Log in to your QNAP device and open Network & Virtual Switch.
- Select Advanced mode.
- Go to Network > Virtual Switch.
- Identify the network segments used by the container network.
- Go to Control Panel > System > Security > Allow/Deny List.NoteIf QuFirewall is installed on your device, ensure it is enabled, then open QuFirewall and add the required network segments to the allow list.
- Ensure that the container network segments are added to the allow list.
 ImportantQNAP strongly recommends adding the following IP ranges to the allow list:
ImportantQNAP strongly recommends adding the following IP ranges to the allow list:10.0.3.0/24,10.0.5.0/24,10.0.7.0/24,172.29.0.0/22,172.30.0.0/22. If Kubernetes services are enabled, also add10.42.0.0/24(Kubernetes Pod Network CIDR).
Checking advanced permission settings
- Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Shared Folders > Advanced Permissions.
- Disable Enable Advanced Folder Permissions.
- Click Apply.
- Go to Control Panel > Privilege > Quota and check user quota settings.NoteQuota settings apply only if quota management is enabled.WarningCheck user quota settings to ensure that no unintended quota restrictions are in place. Accidental quota settings may cause the container to report errors due to storage limitations.
Verifying storage and network configuration
- Go to Storage & Snapshots > Storage > Storage/Snapshots.
- Check available storage capacity.
 NoteIf the status is anything other than Ready, check the disk status for storage errors. For details, see Disk statuses in the QTS or QuTS hero User Guide.
NoteIf the status is anything other than Ready, check the disk status for storage errors. For details, see Disk statuses in the QTS or QuTS hero User Guide.
Checking the network configuration
Ensure the network settings are configured correctly by following these steps:
- Go to Network & Virtual Switch > Network > Interfaces and review the DNS and gateway settings.
- Ensure that the DHCP server can assign IP addresses to containers using a virtual switch. For details, see Virtual switch configurationin the QTS or QuTS hero User Guide.NoteThe Do not assign IP addresses (for special purposes, such as building an external network or isolated network) setting in the virtual switch configuration is intended for specific networking configurations. If you do not require a custom network setup, it is recommended to disable this setting.
However, if you are setting up an external or isolated network, enable it. Be aware that this setting may affect the container's network configuration. For details see Creating a virtual switch in advanced mode in the QTS or QuTS hero User Guide. - Go to Container Station > Preferences > Network Settings and ensure that the container network segments do not conflict with the local environment.ImportantContainer Station uses
10.0.3.0/24,10.0.5.0/24, and10.0.7.0/24as the default IP networks.
Referring to online help and documentation
Some images are open-source, allowing users to modify the source code. If none of the troubleshooting methods resolve the issue, the source image might be incompatible or corrupted. In such cases, QNAP recommends visiting the image website for more information or using alternative images from the same category.
If the image is from the Docker registry, you can find more details on the image’s Overview page. For example, the Ubuntu image in Docker provides quick reference links for further information.





