Setting up a Basic Xsan Environment with QNAP NAS Storage and Fibre Channel
- Introduction to QNAP NAS and Xsan
- Storage Configuration
- Configuring the Xsan MDC (Metadata Controller)
- Configuring an Xsan Client
- Configuring the QNAP NAS
- Xsan Topology
- Configuring Xsan
- Creating an Xsan Volume
- Configuring an Xsan SAN Client with an Xsan Profile
- Configuring an Xsan Client using Terminal
- Mounting an Xsan Volume
Introduction to QNAP NAS and Xsan
Xsan is Apple's clustered file system, which enables multiple macOS workstations to access shared storage space. With Xsan, multiple clients can simultaneously read from or write to the same file while seeing the same file content. Here we will demonstrate a simple setup of Xsan using QNAP NAS storage space over a Fibre Channel (FC) network.

|
Role |
Hardware |
Installed Software |
|---|---|---|
|
Xsan MDC (Metadata Controller) |
|
|
|
Xsan CLIENT |
|
|
|
Shared storage |
QNAP NAS with an FC card installed For NAS and FC card compatibility, see https://www.qnap.com/go/solution/fibrechannel-san. |
The latest version of QTS |
|
Ethernet Switch |
|
N/A |
|
Fibre Channel (FC) Switch |
|
N/A |
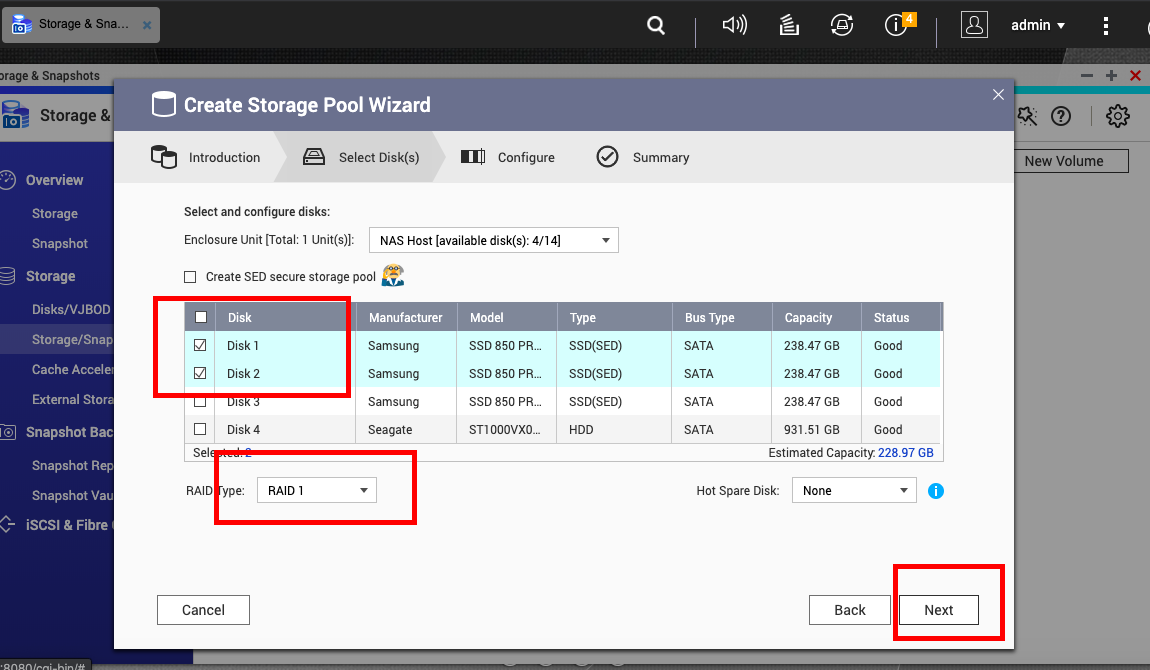
Storage Configuration
An Xsan volume requires three kinds of data storage space: user data, file metadata, and file journal data.
|
Data Type |
Space Consumed |
Recommended RAID Configuration |
Configuration for Demo |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Metadata |
Approximately 10 GB per 10 million files |
RAID 1 |
|
|
File journal |
64 KB to 512 MB per volume |
RAID 1 |
|
|
User data |
Dependent on user |
|
|
Configuring the Xsan MDC (Metadata Controller)
Configuring an Xsan Client
Run the following steps on each client in the Xsan environment.
Configuring the QNAP NAS
Xsan Topology
The following is an example of a basic Xsan topology:
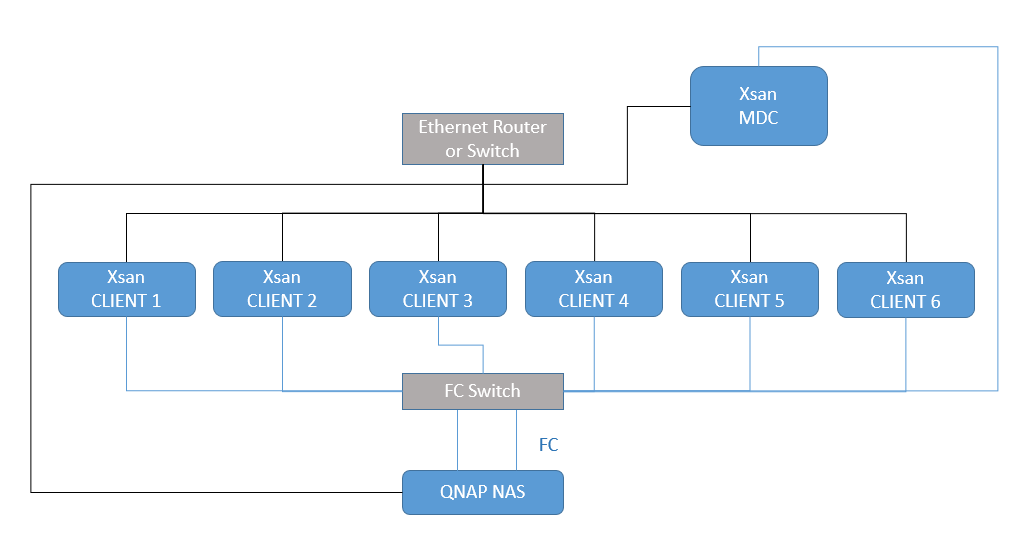
Here is a simplified version where the MDC and a client are connected directly to the FC ports on the NAS.

- Fibre Channel (FC)
- Connect all the clients and the NAS with FC cables.
- Performance is dependent on the bandwidth of the NAS FC card, SFP transceivers, FC cables, Thunderbolt to FC adapter, and FC switch.
- Ethernet
- Connect all the computers and the NAS to a Gigabit router or switch with Ethernet cables.
- Apple recommends creating three independent Ethernet networks which connect all computers in the Xsan environment: Internet, Distributed LAN Client (DLC), and metadata. For simplicity, in this tutorial we only create the metadata network.
- Assign a static IP address to each computer in the Xsan network, and ensure all computers have valid DNS entries.
Tip: If you want to use a DHCP router to assign IP addresses, you can reserve each IP address as static in the router’s setting.
Configuring Xsan
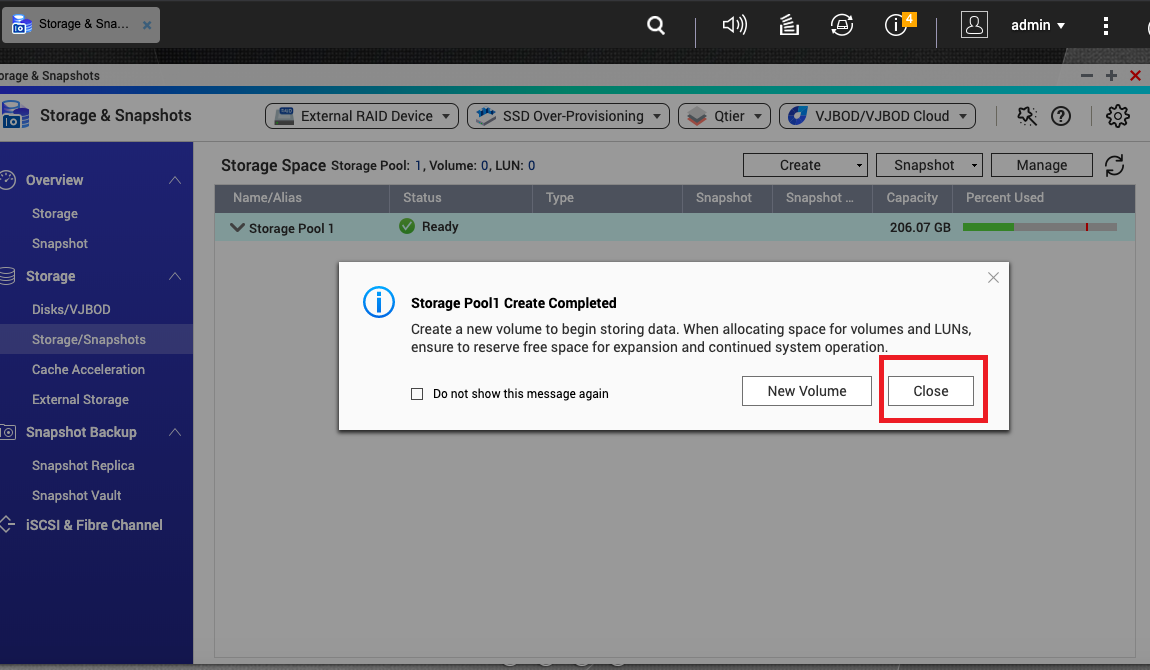
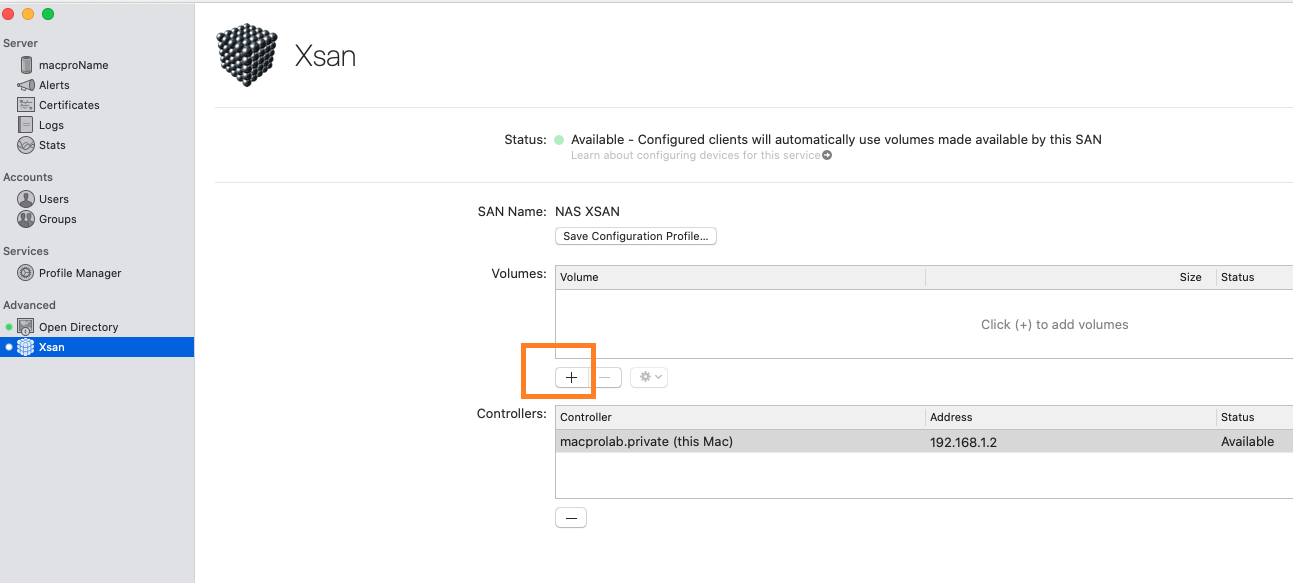
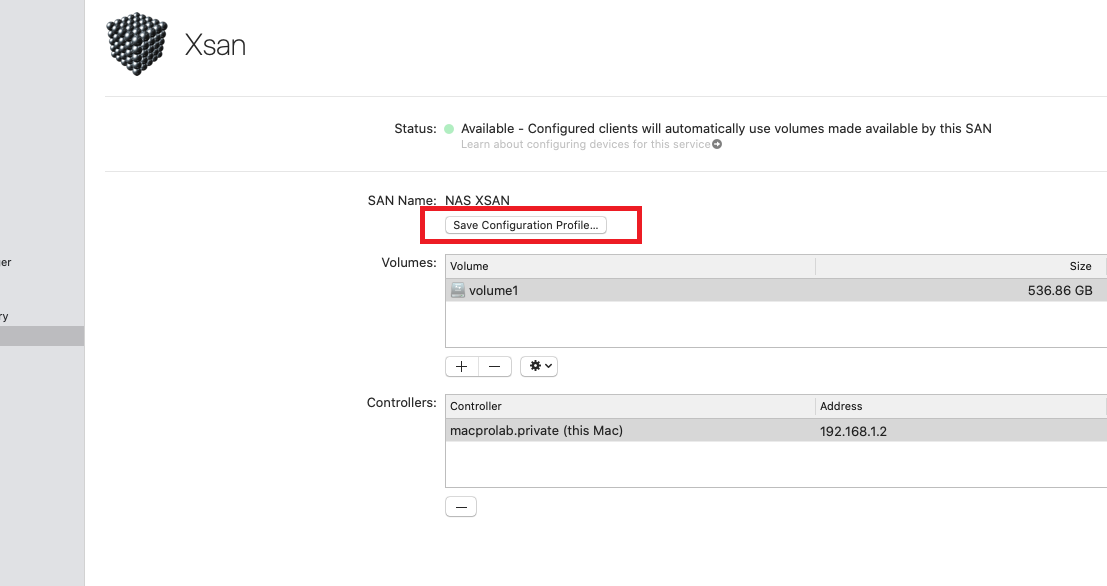
Creating an Xsan Volume
The volume is created. The new volume appears in the Xsan volume list.
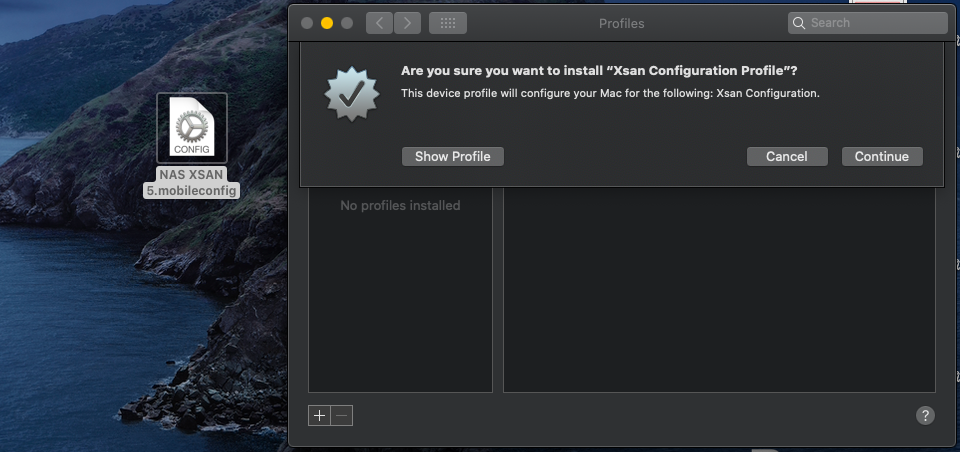
Configuring an Xsan SAN Client with an Xsan Profile
Xsan configures clients by giving them a configuration profile which is generated by the SAN. There are two methods; manually apply the profile, or use Profile Manager. Here we will manually apply the configuration profile to the client. Apply to the following steps to each client in the Xsan environment.
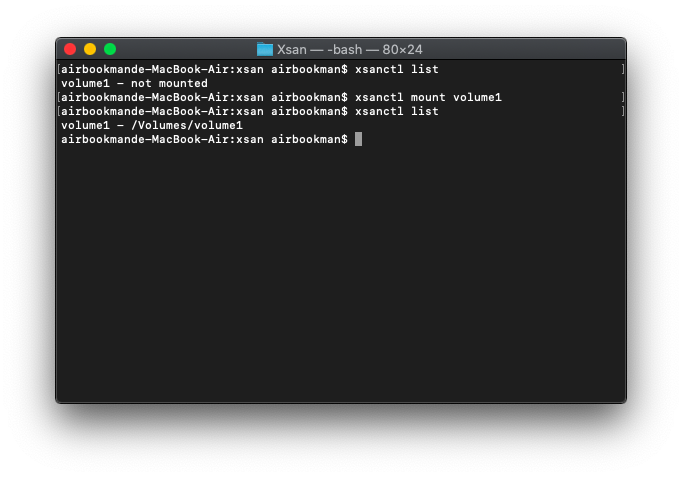
Configuring an Xsan Client using Terminal
When configuring a client with the Xsan configuration profile, you might encounter an error such as CPDomainPlugin:101. If you encounter this error, try the following steps as a workaround.
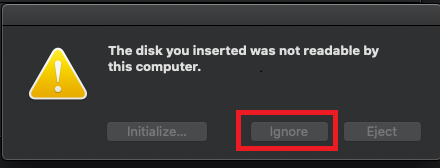
Mounting an Xsan Volume
Perform these steps on every client and on the MDC.
The mounted volume appears in Finder.