Applicable Products
- QuWAN Orchestrator
- QuRouter 2.4.4 and later versions
Details
To utilize QuWAN services, configure the necessary service ports on the third-party firewall device.
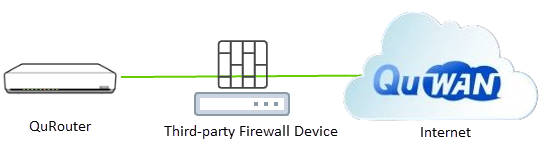
The network topology depicted in the image illustrates a hub-and-edge SD-WAN deployment leveraging QNAP's QuWAN infrastructure. The key components and their roles are as follows:
QuRouter (QNAP router): Positioned at the network perimeter, this device connects to a third-party firewall device and functions as either a hub for internal traffic or an edge device for external connectivity, depending on the deployment. Third-party firewall: Situated behind the QNAP router, this firewall enforces security policies, regulates network traffic, and manages access control.
Best Practices
To ensure seamless connectivity to QuWAN Orchestrator, configure the following firewall rules on all routers in your network topology before accessing Orchestrator from a client device (such as a browser). These settings enable secure VPN communication, proper traffic routing, and uninterrupted access to QuWAN services.
1. Configure Firewall Rules for QuWAN Orchestrator
- Source: Any
- Protocol: TCP
- Destination ports: 8883 (MQTT), 443 (HTTPS)
2. Configure Firewall Rules for QuWAN QBelt VPN Server
| Traffic Type | Source | Protocol | Source Ports | Destination | Destination Ports | Action |
|---|
| Outbound | Click Define to specify the source connection | UDP | 5533 (QuWAN QBelt VPN Server) | Any | - | Allow |
| Inbound | Click Define to specify the remote device details | UDP | Any | - | 5533 (QuWAN QBelt VPN Server) | Allow |
To add a new firewall rule in QuWAN Orchestrator, see the "Adding a device firewall rule" topic in the QuWAN and QuWAN Orchestrator Web Help.
Note
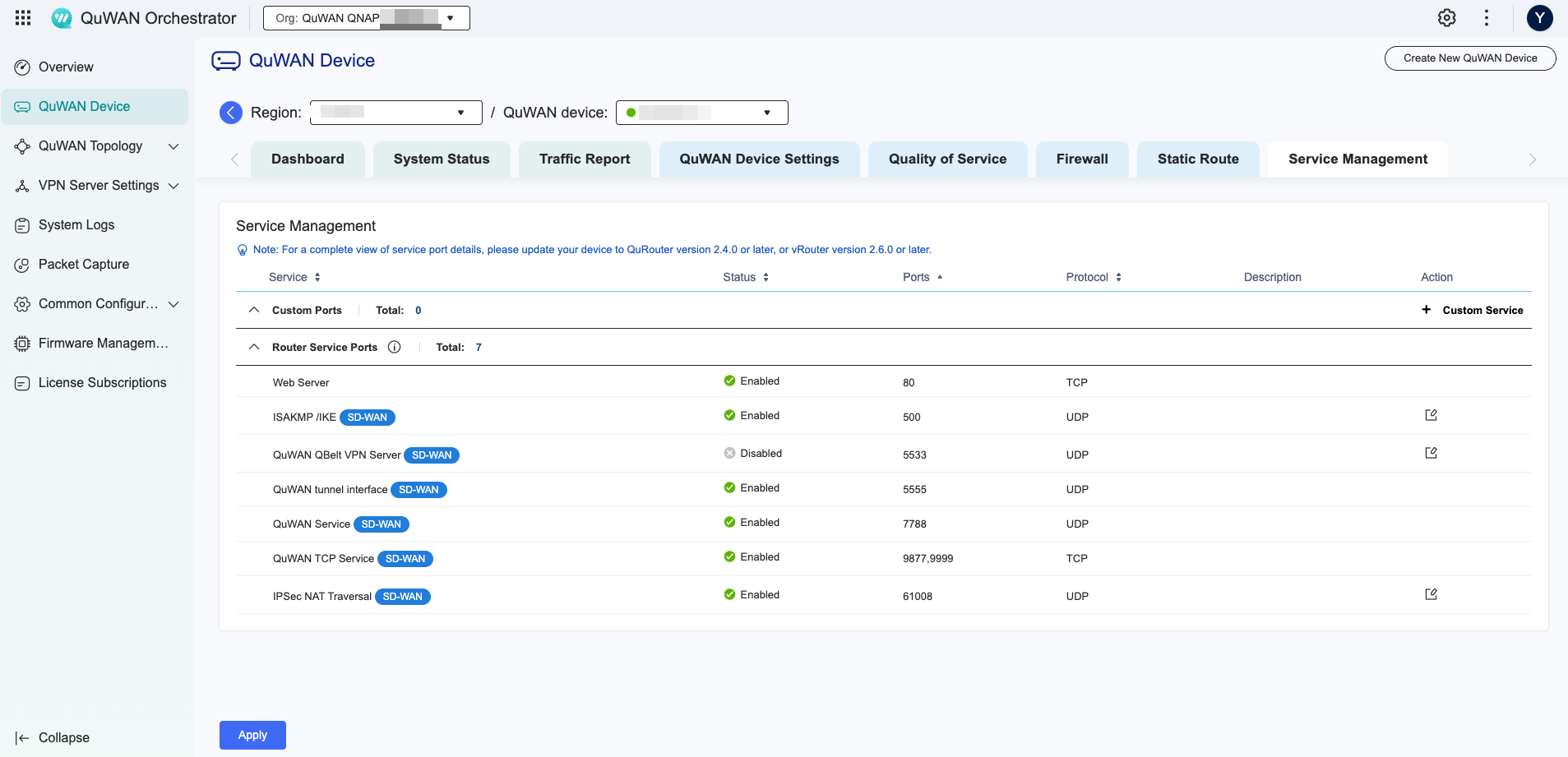
The default port for QuWAN QBelt VPN is 5533, but it can be changed. To check the router service ports in QuWAN Orchestrator, select your organization and device, and then go to Service Management.
3. Configure Firewall Rules for Mesh VPN Site-to-Site Traffic
When using QuRouter in a mesh VPN setup, you must configure firewall rules on a third-party firewall device to allow site-to-site VPN traffic. These rules ensure that IPSec communication between the hub and edge sites is not blocked, enabling secure VPN tunnel establishment.
On the third-party firewall device, allow inbound and outbound UDP traffic on the following ports:
- 500 (ISAKMP/IKE): Used for key exchange in IPSec VPN connections.
- 4500 (IPSec NAT Traversal): Used when VPN traffic traverses NAT devices.
- 61001-61999 (Dynamic high ports for IPSec NAT Traversal): Required for certain IPSec configurations.
Configure the firewall rules as follows:
- Inbound traffic: Allow VPN packets from remote sites to reach the firewall.
- Outbound traffic: Permit VPN packets to be sent to remote sites without interference.
Properly configuring these rules on the third-party firewall device ensures uninterrupted VPN connectivity between mesh sites.
| QuRouter Role | Hub | Edge |
|---|
| Protocol | UDP | UDP |
| Inbound traffic | - Source ports: 500 (ISAKMP/IKE), 4500/61xxx* (IPSec NAT Traversal)
- Destination ports: 500 (ISAKMP/IKE), 4500* (IPSec NAT Traversal)
| - Source ports: 500 (ISAKMP/IKE), 4500* (IPSec NAT Traversal)
- Destination ports: 500 (ISAKMP/IKE), 61xxx* (IPSec NAT Traversal)
|
| Outbound traffic | - Source ports: 500 (ISAKMP/IKE), 4500* (IPSec NAT Traversal)
- Destination ports: 500 (ISAKMP/IKE), 4500/61xxx* (IPSec NAT Traversal)
| - Source ports: 500 (ISAKMP/IKE), 61xxx* (IPSec NAT Traversal)
- Destination ports: 500 (ISAKMP/IKE), 4500* (IPSec NAT Traversal)
|
Note
- * The default port for hubs and edge devices is 4500.
- * The system selects a random port between 61001-61999. To check the router service ports, select your organization and device in QuWAN Orchestrator, and then go to Service Management and review the port details in IPSec NAT Traversal.
Important
To determine if additional IPSec NAT traversal ports are required, select your organization and device in QuWAN Orchestrator, and then go to Service Management.
4. Allow IP Ranges for QuWAN Communication
To ensure proper communication between QuWAN Orchestrator and your existing firewall services, it is essential to configure your firewall and router to allow specific IP ranges related to QuWAN. The router plays a crucial role by routing traffic between your local network and external networks, while the firewall filters and permits necessary QuWAN-related traffic to ensure secure and uninterrupted communication. Without proper configuration, you may encounter disruptions.
Follow the steps below to add the necessary QuWAN-related IP ranges to your firewall's allow list:
- QuWAN VPN tunnel
- Add
198.19.0.0/16 to your firewall's allow list to ensure that VPN tunnel connections established by QuWAN are not blocked:
- QuWAN LAN IP subnet
- Identify the LAN IP subnet of your QuWAN deployment and include it in your firewall's allow list.
- To locate the LAN IP subnet, navigate to QuWAN Device > System Status > Network > LAN Details in the QuWAN Orchestrator interface.
By configuring both your firewall and router with these settings, you can ensure proper traffic routing, secure filtering, and uninterrupted communication between QuWAN services and your network, minimizing potential disruptions caused by blocked traffic.
For further assistance, refer to the QuWAN Orchestrator documentation or contact QNAP Customer Service.
Additional Notes
To enable internet pings from LAN to WAN, add a firewall rule:
- Destination: Click Define to specify the internet gateway address
- Protocol: ICMP
- Source: Any (allows traffic from any device on your LAN)
- Destination: Your LAN subnet (e.g., 192.168.60.1/24)
- Action: Allow
If a device remains offline despite an active WAN connection, verify that ports 8883 (MQTT) and 443 (HTTPS) are not blocked by the firewall.
For detailed instructions on configuring firewall rules in QuWAN Orchestrator, see the Firewall and Traffic Mapping section in the QuWAN and QuWAN Orchestrator Web Help.
To modify service ports, perform the following actions:

Further Reading
Produtos Aplicáveis
QuWAN Orchestrator
Detalhes
Este FAQ aborda métodos comuns de configuração de Firewall para definições correspondentes quando a conexão VPN mesh falha:
Melhores Práticas
Para procedimento detalhado de criação ou modificação de uma regra de Firewall , consulte Configurações de Firewall no Ajuda online do QuWAN e QuWAN Orchestrator .
1. Desconectado de QuWAN Orchestrator
Problema: Você não pode conectar à interface de gestão do QuWAN Orchestrator .
Solução: Certifique-se de que o Firewall permite comunicação na porta 8883 (TCP) com o QuWAN Orchestrator usando a seguinte configuração.
- Fonte: Clique em Definir para especificar o endereço IP ou sub-rede do QuWAN Orchestrator
- Protocolo: TCP
- Portas de Origem: 8883
- Destino: Qualquer
- Ação: Permitir
2. Desconectado do servidor VPN QuWAN QBelt
Problema: Você não pode estabelecer uma conexão VPN com o servidor VPN QuWAN QBelt.
Solução: Certifique-se de que o Firewall permite comunicação com o QuWAN Orchestrator usando as regras configuradas a seguir.
- Regra 1 (Tráfego de entrada):
- Fonte: Clique em Definir para especificar a conexão de origem
- Protocolo: UDP
- Portas de Origem: 5533
- Destino: Qualquer
- Ação: Permitir
- Regra 2 (Tráfego de saída):
- Fonte: Clique em Definir para especificar os detalhes do dispositivo remoto
- Protocolo: UDP
- Portas de Origem: Qualquer
- Destino: 5533
- Ação: Permitir
3. Tráfego VPN Mesh Site-to-Site Bloqueado
Problema: A transferência de dados entre o VPN mesh site-to-site está bloqueada.
Solução: Para garantir que o tráfego utilizado pelo serviço Mesh VPN possa passar pelo Firewall , crie duas regras de Firewall permitindo as portas UDP necessárias.
- Regra 1 (Tráfego de entrada):
- Origem: Clique em Definir para especificar a conexão de origem
- Protocolo: UDP
- Portas de Origem: 500, 4500 (Vá à página de Gestão de Serviço para determinar se outras portas de Traversal NAT IPSec são necessárias), 5555, 7788
- Destino: Qualquer
- Ação: Permitir
- Regra 2 (Tráfego de saída):
- Origem: Qualquer
- Protocolo: UDP
- Portas de Origem: Qualquer
- Destino: 500, 4500 (Vá à página de Gestão de Serviço para determinar se outras portas de Traversal NAT IPSec são necessárias), 5555, 7788
- Ação: Permitir
4. Pedidos de Ping Falhados de Dispositivos LAN
Problema: Não consegue fazer ping à internet a partir dos seus dispositivos LAN.
Solução: Garanta que a regra de Firewall permite tráfego ICMP da sua rede LAN para a internet.
- Destino: Clique em Definir para especificar o endereço do gateway de internet
- Protocolo: ICMP
- Origem: Qualquer (permite tráfego de qualquer dispositivo na sua LAN)
- Destino: A sua sub-rede LAN (ex., 192.168.60.1/24)
- Ação: Permitir
Notas Adicionais
- Substitua a sub-rede LAN 192.168.60.1/24 pelo endereço real da sua sub-rede LAN.
- A porta de Traversal NAT IPSec depende do papel do dispositivo QuWAN:
- Hub : A porta padrão é 4500. Adicione esta porta à lista de portas de origem na regra 2 (saída) se aplicável.
- Edge : Usa um número de porta aleatório entre 61001-61999. Permita todas as portas neste intervalo para tráfego de origem da interface WAN na regra 2 (saída) se necessário.