How can I use MARS (Multi-Application Recovery Service) to clear space in my Google Photos storage?
Applicable Products
MARS 1.1 and later
About MARS (Multi-Application Recovery Service)
MARS (Multi-Application Recovery Service) is a comprehensive backup and disaster recovery solution for applications and data on your QNAP NAS. It allows you to back up and restore individual services and service data. Backups and restorations are performed by backup and restore jobs which can be run manually or automatically by schedule. Backups can also be managed through versioning, and services/data can be restored with any version. MARS also has integrated logs, allowing you to review all backup/restore activity.
Overview
MARS (version 1.1 and later) can help you manage your limited Google Photos storage space without losing any data. After using MARS to backup photos to your NAS, you can safely delete the photos from your Google account in order to stay within your Google Photos storage limit. The photos can be restored from your NAS to your Google account at any time with MARS.
- Video backups:
- MARS may not be able to access videos immediately after uploading them to Google Photos. The backup job may fail, or some files may be skipped. In these cases, wait for a period of time and try the backup job again.
- Videos higher than 1080p and 30FPS will be backed up in 1080p and 30 FPS.
- Image backups:
- Google Photos may alter the pixel format or metadata when MARS retrieves the images. These alterations may change the final file size of the backup.
- Images with the YUV444 color model will be converted to the YUV420 color model. Images with the YUV422 or RGB24 color models will not be converted.
- Location data, including GPS coordinate information, may be removed from certain images.
Steps
To back up your Google Photos data with MARS, first create a Google Photos service for your Google Photos account, then create a backup job. For restoring photos, see “Creating a restore job” in MARS (Multi-Application Recovery Service) User Guide?
1. Create a Google Photos Service
Only one Google Photos service can be created per Google account.
- Log in to your NAS as an administrator and open MARS.
- Create a Google Photos service:
- Go to Applications → Google Photos.
- Click + Add Service.

- Enter a name for your Google Photos service
- Click Connect to Google Photos.
The Sign in with Google window appears.
- Select your Google account.
You will be asked to allow MARS to access your Google Account.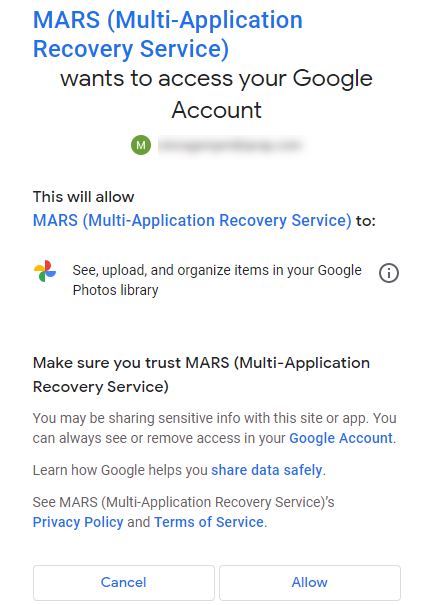
- Select Allow.
A green check mark appears indicating MARS has successfully connected to your Google Account.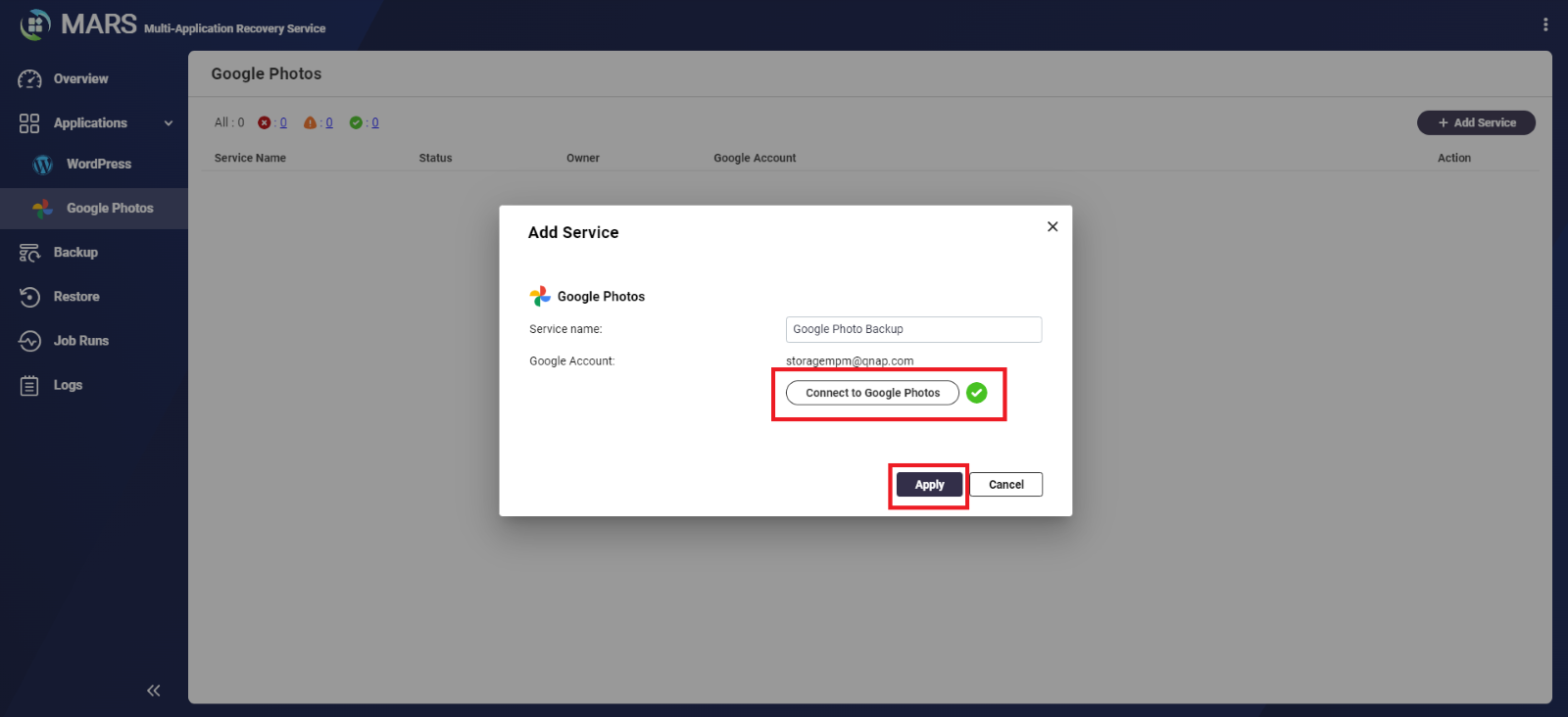
- Click Apply.
- Your Google Photos service is created:
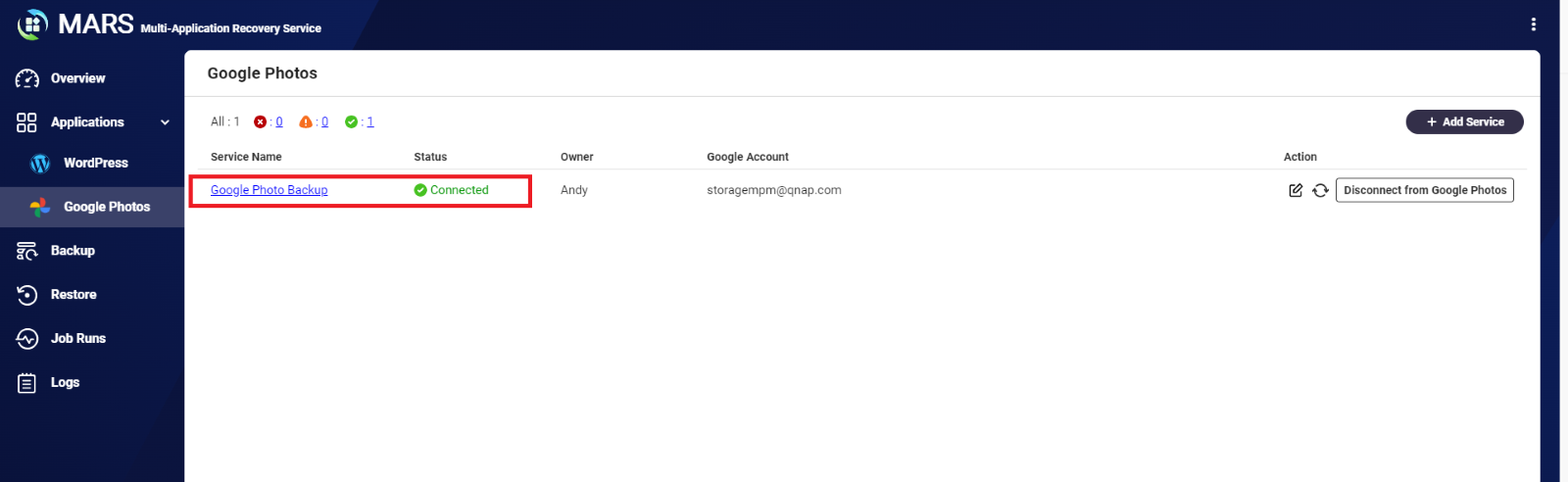
2. Create a Backup Job
- Go to Backup.
- Click Create Backup Job.
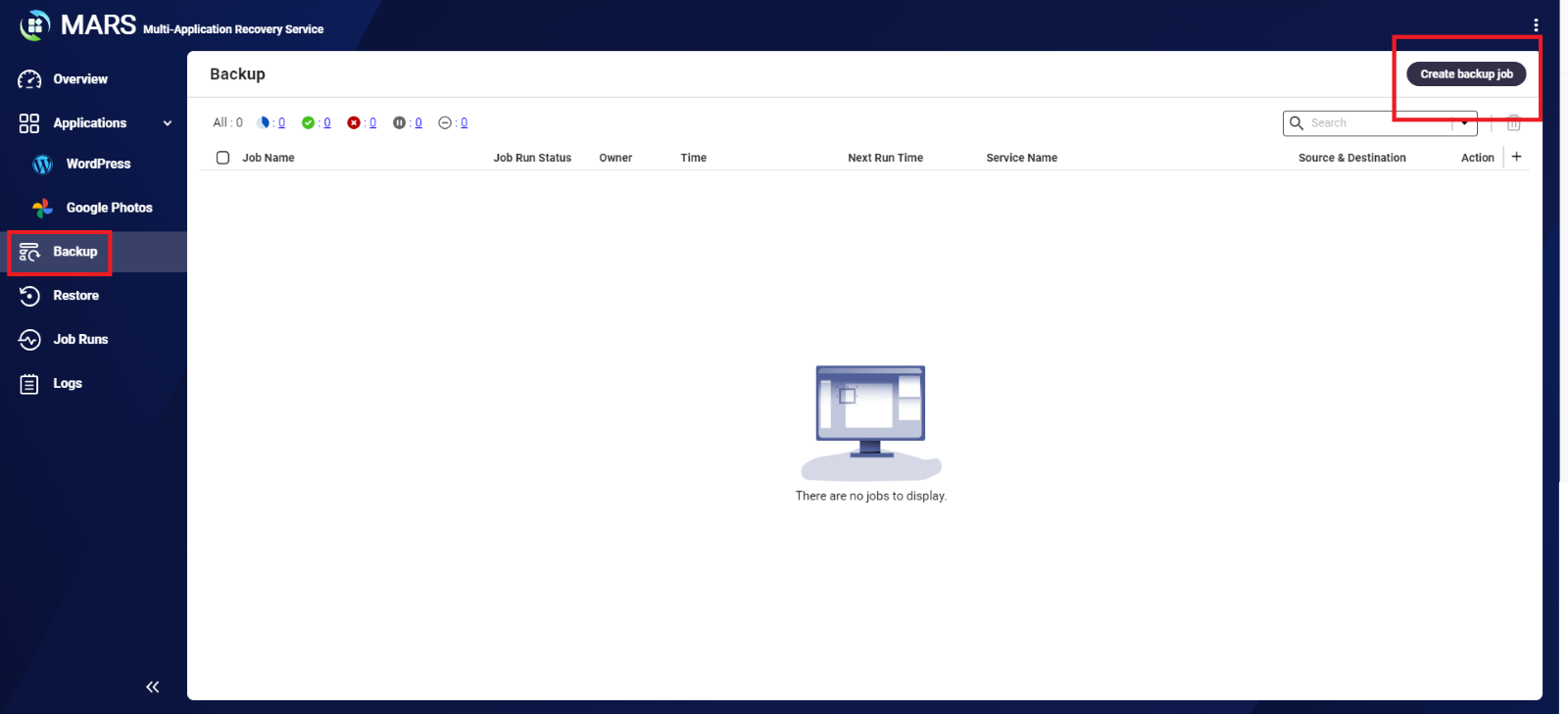
- Under Job Information, specify the following:
Field Description Service type Select Google Photos Job name The name of the backup job Job description A description of the job - Under Source and Destination, specify the following:
- Source: Click Browse and select the Google Photos service you created previously.
- Destination: Click Browse and select the NAS folder where your Google Photos data will be stored.
- Under Backup Files, specify one of the following options:
- All: All photos in your Google Photos account are backed up.
- Specify albums: Only photos belonging to specified albums are backed up.
- Optional: Create a backup schedule to run the backup job automatically. For details, see "Creating a backup job” in How to use Multi-Application Recovery Service (MARS) ?
- Optional: Enable version management to backup multiple versions of your Google Photos data. For details, see "Creating a backup job” in How to use Multi-Application Recovery Service (MARS) ?
- Click Backup Now.
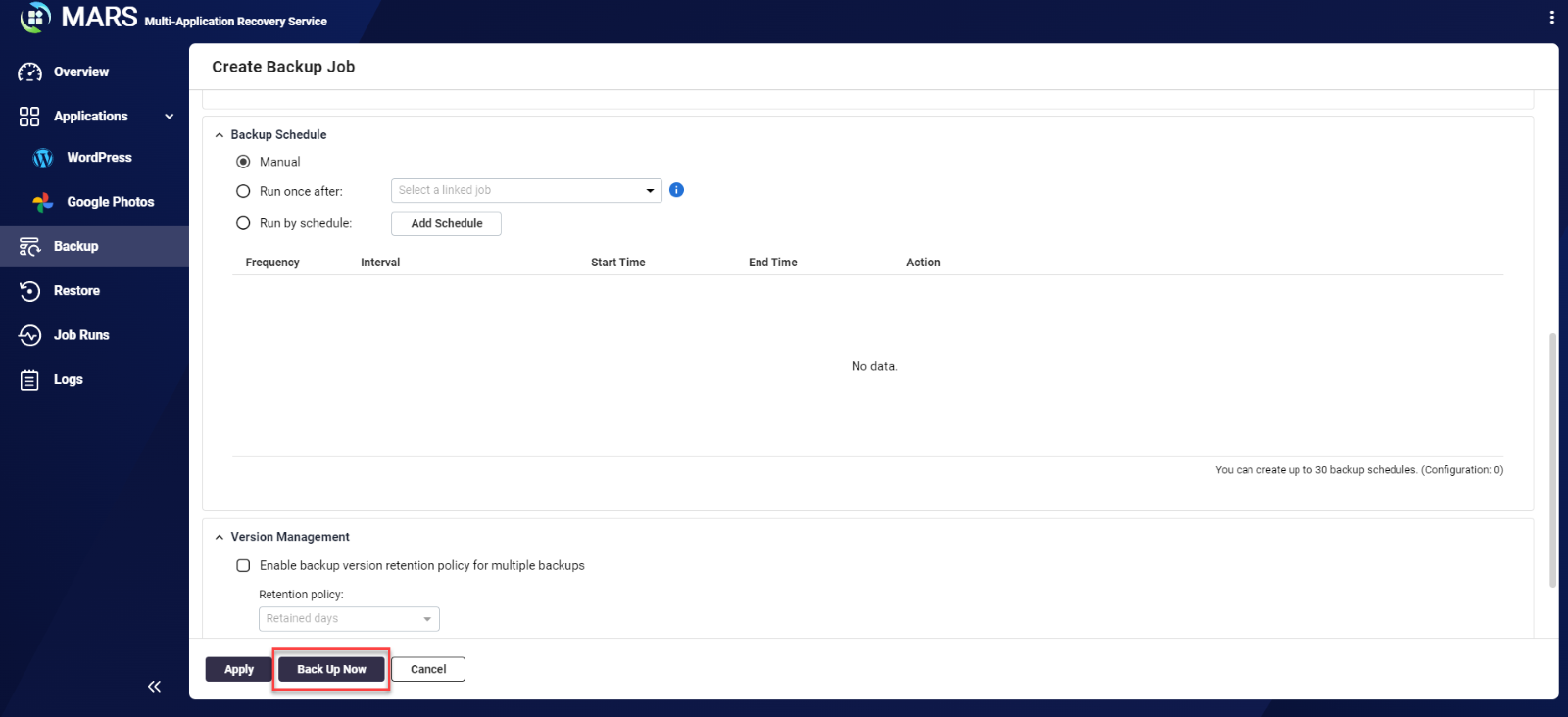
A backup job will be created and immediately begin backing up your photos.
After the backup job completes, you can view the photos by the opening the destination folder with File Station. The sub-folders created correspond to your Google Photos albums.
Further Reading
Why does MARS backup media files from Google Photos in a different format or resolution?





